Science
Scientists Uncover 1 Million-Year-Old DNA in Mammoth Remains

Researchers have discovered DNA dating back over one million years in remains of woolly mammoths. This groundbreaking finding, led by a team from the Centre for Palaeogenetics in Sweden, reveals some of the oldest microbial DNA ever identified. In addition, the study highlights bacteria that may have contributed to disease in these long-extinct mammals.
Significant Discoveries from Ancient Remains
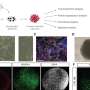
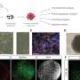
The international team analyzed microbial DNA from 483 mammoth specimens, sequencing 440 for the first time. Among these, a steppe mammoth that lived approximately 1.1 million years ago provided crucial insights. By employing advanced genomic and bioinformatic techniques, researchers were able to differentiate between microbes that coexisted with the mammoths and those that invaded their remains post-mortem.
Dr. Benjamin Guinet, the study’s lead author, remarked, “Imagine holding a million-year-old mammoth tooth. What if I told you it still carries traces of the ancient microbes that lived together with this mammoth?” This discovery pushes the boundaries of microbial DNA research, opening new avenues to explore how these microorganisms evolved alongside their hosts.
The team identified six microbial groups consistently associated with mammoths, including relatives of Streptococcus, Actinobacillus, Pasteurella, and Erysipelothrix. Some of these microbes are suspected to have been pathogenic. For instance, one bacterium related to Pasteurella is closely associated with a pathogen responsible for fatal outbreaks in African elephants. Given that African and Asian elephants are the closest living relatives of mammoths, this raises questions about the potential vulnerability of mammoths to similar infections.
Implications for Understanding Ancient Ecosystems
The researchers successfully reconstructed partial genomes of Erysipelothrix from the 1.1-million-year-old steppe mammoth, marking the oldest known instance of host-associated microbial DNA ever recovered. This achievement enhances our understanding of the interactions between ancient hosts and their microbiomes.
Dr. Tom van der Valk, a senior author of the study, explained, “As microbes evolve fast, obtaining reliable DNA data across more than a million years was like following a trail that kept rewriting itself.” His comments underline the challenges faced in studying ancient remains and their associated biological insights.
While determining the exact impact of these microbes on mammoth health is complicated due to DNA degradation and the lack of comparative data, the findings provide an unprecedented look into the microbiomes of these ancient giants. Published in the journal Cell, the research indicates that some microbial lineages coexisted with mammoths for hundreds of thousands of years, spanning wide geographic ranges and evolutionary timelines, from over one million years ago to the extinction of woolly mammoths on Wrangel Island around 4,000 years ago.
Professor Love Dalén, an ancient DNA expert at the Centre for Palaeogenetics, noted, “This work opens a new chapter in understanding the biology of extinct species. Not only can we study the genomes of mammoths themselves, but we can now begin to explore the microbial communities that lived inside them.”
This research represents a significant milestone in palaeogenetics, offering new perspectives on how ancient microorganisms may have influenced the evolution, health, and eventual extinction of mammoths in Pleistocene ecosystems.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2