Science
Scientists Investigate Soft Matter Behavior in Space Environments

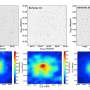
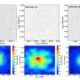
Recent research has shifted focus to the behavior of soft matter, such as creams and drugs, in space. Scientists from the European Space Agency and NASA are studying how materials like gels and emulsions react in microgravity environments aboard the International Space Station (ISS). This exploration is crucial for understanding the stability and efficacy of various products used in space missions.
Soft matter encompasses a range of materials that can change over time, affecting their shelf life and effectiveness. This includes everyday items such as sunscreen and mayonnaise, as well as pharmaceutical drugs. As these materials are subjected to the unique conditions of space, including 0% gravity, their properties may alter significantly.
Understanding Soft Matter in Microgravity
The research led by Professor Fabrice M. J. J. V. D. K. aims to elucidate the mechanisms that influence the behavior of soft matter in space. Initial findings indicate that the stability of these materials can increase by as much as 10% when exposed to microgravity conditions. This insight could have profound implications for the formulation of products used in long-duration space missions, where reliability and longevity are paramount.
The characteristics of soft matter, particularly its disordered structures, are susceptible to changes due to environmental factors. In microgravity, the absence of gravitational forces alters the dynamics of these materials, leading to different interaction patterns. This research is paving the way for improved formulations that can withstand the rigors of space travel.
Implications for Future Space Missions
As space agencies prepare for extended missions to destinations such as Mars, understanding the behavior of materials in space becomes increasingly important. The research conducted on the ISS provides valuable data that can influence the development of more effective and stable products for astronauts.
For instance, the effectiveness of sunscreen is critical for protecting astronauts from harmful solar radiation during spacewalks. Similarly, the stability of medications is vital for maintaining the health of crew members in isolated environments. By investigating how these products behave in microgravity, researchers can enhance their formulations to ensure maximum efficacy.
The findings from this research not only benefit space exploration but also have potential applications on Earth. Understanding soft matter behavior in extreme conditions can lead to advancements in various industries, including food technology and pharmaceuticals.
As this research evolves, it promises to unlock new possibilities for both space travel and everyday products, demonstrating the interconnectedness of scientific inquiry across different fields. The ongoing studies aboard the ISS will continue to shed light on the complexities of soft matter, ultimately contributing to the safety and well-being of those venturing beyond our planet.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2