Science
New Findings on Neolithic Human Sacrifice at Shimao Gate

A recent study published in the journal Nature on November 26, 2023, has revealed significant insights into the Neolithic population of Shimao, a key archaeological site in China. The research focused on the analysis of ancient DNA from individuals who lived at Shimao, uncovering genetic connections to southern settlements and indicating practices of human sacrifice through the discovery of mass burials of male individuals.
Situated in the northern region of Shaanxi province, Shimao is recognized as one of the most important late Neolithic settlements in China. The site, which dates back approximately 4,500 years, has previously attracted attention for its impressive architecture and sophisticated society. This new genetic study adds another layer of understanding to the social and cultural dynamics of its inhabitants.
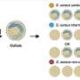
The research team analyzed DNA samples from remains found in burial pits, revealing a complex picture of kinship and population structure. The findings suggest that the people of Shimao had genetic ties to communities in southern China, indicating possible migration patterns or interactions between distinct groups during the Neolithic period.
One of the most striking discoveries was the evidence of mass burials involving males, which the researchers associated with ritualistic human sacrifice. This practice may have been linked to religious or social beliefs prevalent at the time, reflecting the intricate worldview of the Neolithic society at Shimao.
The study’s authors emphasize that understanding these burial practices provides valuable insights into the social organization and cultural expressions of ancient communities. The implications of these findings extend beyond Shimao, as they contribute to the broader narrative of human sacrifice in early Chinese civilizations and their developing social hierarchies.
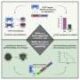
Researchers utilized advanced genetic sequencing techniques to extract and analyze DNA from the ancient remains. These methods allowed for a clearer understanding of ancestry and lineage, aiding in the reconstruction of historical population dynamics.
The results of this study not only enrich our understanding of the Shimao site but also highlight the complexities of human interactions in Neolithic China. As scholars continue to piece together the lives of ancient peoples, this research underscores the importance of multidisciplinary approaches that combine archaeology, genetics, and anthropology.
In summary, the findings from Shimao represent a significant advancement in the study of Neolithic societies, revealing intricate details about their kinship systems, migrations, and cultural practices. As more research is conducted, the story of Shimao and its people will likely continue to evolve, offering deeper insights into the ancient world.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoHarmonic Launches AI Chatbot App to Transform Mathematical Reasoning
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride