Science
Astronomers Unveil Potential Dark Matter Candidate in Distant Cosmos
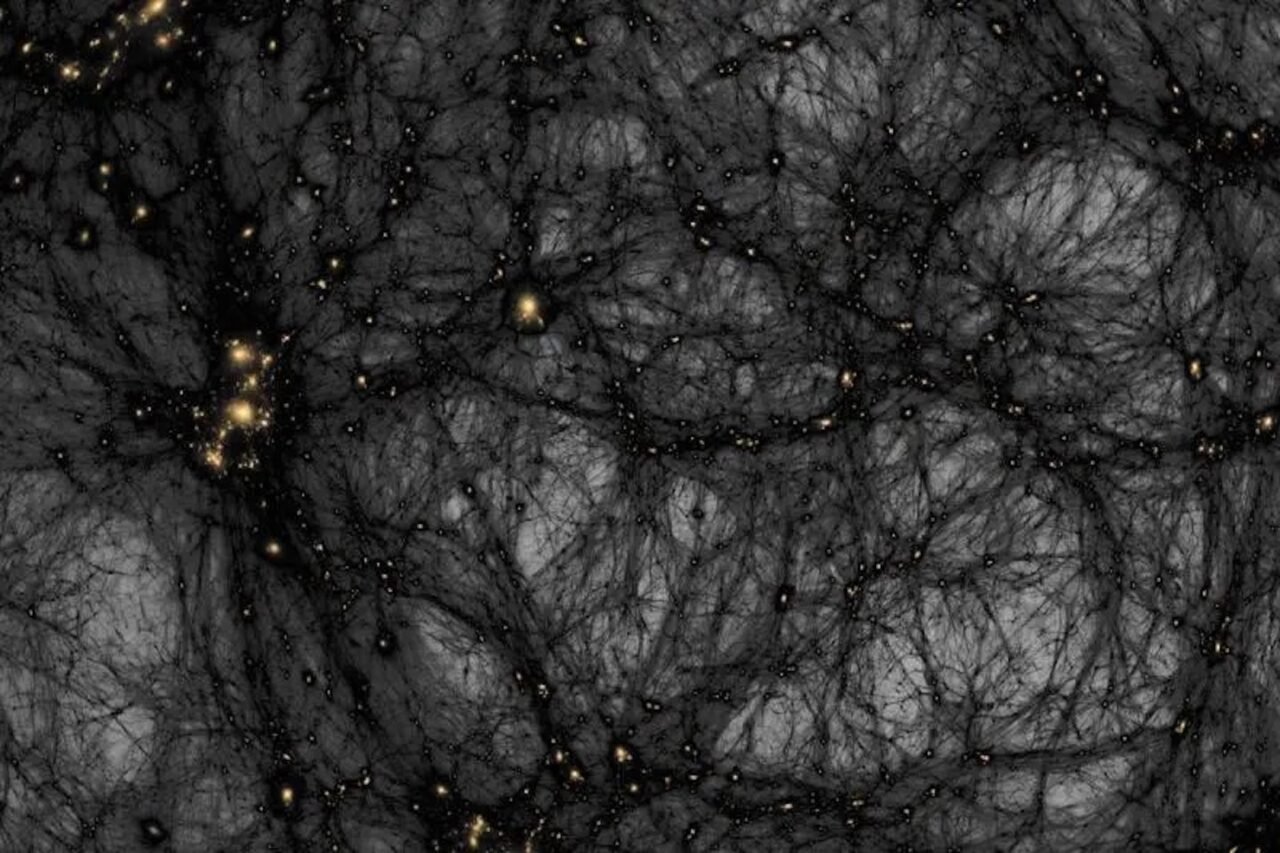
Astronomers have identified an exceptionally faint and low-mass object in the distant universe, raising the possibility that it may be composed of dark matter. This elusive substance accounts for nearly 30% of the universe’s total mass. The research team, whose findings were published in the journal Nature Astronomy on March 15, 2024, believes this could be the lowest-mass dark object ever detected, although its exact nature remains uncertain.
The discovery was made using a technique known as gravitational lensing, which measures how an object’s gravity affects light that passes near it. This method acts like a cosmic magnifying glass, allowing astronomers to detect faint objects that would otherwise remain invisible. According to Chris Fassnacht, a professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the University of California, Davis, “Finding low-mass objects such as this one is critical for learning about the nature of dark matter.”
Unraveling Cosmic Mysteries
To carry out this groundbreaking study, researchers combined data from multiple observatories, effectively creating an Earth-sized telescope. The newly discovered object was so small that it only caused a minor distortion in the gravitational lensing effect of a distant galaxy. Fassnacht described the achievement as “impressive,” noting the challenge of detecting such a low-mass object from such vast distances.
Though the object’s true nature is not yet confirmed, researchers speculate that it could either indicate the presence of dark matter or represent a very small and dense dwarf galaxy. Dark matter serves as the fundamental structure that binds galaxies and galaxy clusters together, making up about 27% of all matter in the cosmos, as reported by NASA. Despite its significant presence, dark matter remains invisible, with its existence inferred through its gravitational effects on ordinary matter.
Insights into Dark Matter
Dark matter’s role is crucial in understanding the universe. It constitutes most of the mass in galaxies and galaxy clusters. While dark matter does not interact with light, its gravitational influence can bend light from distant galaxies, creating a lensing effect. If the newly discovered object is indeed comprised of dark matter, it would be approximately 100 times smaller than any previously identified clump of dark matter.
The discovery aligns with a hypothesis known as the cold dark matter theory. This theory posits that dark matter consists of weakly interacting, slow-moving particles that cluster together through gravitational attraction. Devon Powell, the lead author of the study from the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics in Germany, stated, “Given the sensitivity of our data, we were expecting to find at least one dark object. Having found one, the question now is whether we can find more and whether the numbers will still agree with the models.”
As the research continues, scientists hope that further investigations will yield additional discoveries that could illuminate the mysteries surrounding dark matter and its role in the evolution of the universe.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide