Health
Anxiety and Insomnia Linked to Lower Immune Function

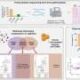
Emerging research indicates that anxiety and insomnia may significantly reduce the count of natural killer (NK) cells, potentially impairing the immune system’s ability to function effectively. This discovery could have profound implications for understanding how mental health directly influences physical health.
Naturally occurring in the body, NK cells serve as a crucial component of the immune system. They act as the first line of defense against invading pathogens, foreign substances, and cells that have been infected. By targeting and eliminating these threats in their early stages, NK cells help to prevent the escalation of infections and diseases. A diminished count of these cells can lead to immune dysfunction and a heightened risk of various illnesses.
Researchers from the **University of Health Sciences** conducted a study to assess the relationship between mental health conditions, specifically anxiety and insomnia, and NK cell levels. They found that individuals experiencing high levels of anxiety and chronic sleep disturbances exhibited a notable decrease in NK cell activity. This reduction not only compromises the body’s immediate immune responses but also raises concerns about long-term health implications.
The study highlights the need for a holistic approach to health that encompasses both mental and physical well-being. Previous scientific literature has recognized the connection between stress and immune function, but this new evidence specifically points to anxiety and sleep issues as detrimental factors in NK cell viability.
The Role of Natural Killer Cells
Natural killer cells are essential for maintaining immune health. They can be found circulating in the bloodstream or residing in tissues and organs, where they remain vigilant against threats. A healthy count of NK cells is critical for the body to fend off diseases effectively. When the number of these cells is insufficient, the body becomes more vulnerable to infections, making it imperative to address factors that can lead to their depletion.
The findings from the University of Health Sciences study suggest that managing anxiety and improving sleep quality may be crucial strategies for enhancing immune function. Simple lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and proper sleep hygiene, could contribute positively to both mental and physical health.
With the ongoing global challenges posed by various infectious diseases, understanding the links between mental health and immune response becomes increasingly important. As studies continue to evolve, healthcare professionals may need to adopt a more integrated approach that prioritizes mental wellness as a pivotal aspect of overall health.
In conclusion, the connection between anxiety, insomnia, and immune function underscores the importance of addressing mental health concerns. As research progresses, there is potential for developing targeted interventions that can support not only mental well-being but also enhance the body’s natural defenses against illness.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBreakthroughs and Challenges Await Science in 2026
-

 Technology8 months ago
Technology8 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoTop 10 Penny Stocks to Watch in 2026 for Strong Returns
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoJapanese Study Finds Rose Oil Can Increase Brain Gray Matter
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Education6 months ago
Education6 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications