Science
Researchers Explore Repurposed Drugs to Reverse Alzheimer’s in Mice

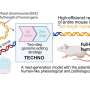
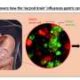
Alzheimer’s disease continues to challenge researchers and families alike, afflicting millions with memory loss and cognitive decline. In a promising development, a team from the University of Copenhagen has demonstrated that arginine, a common amino acid used primarily for managing high blood pressure, shows potential in reversing signs of dementia in mice. The findings, published in a peer-reviewed journal, indicate that this over-the-counter supplement can clear brain plaques associated with Alzheimer’s and restore cognitive function in rodent models.
The study involved administering arginine to mice genetically engineered to exhibit Alzheimer’s pathology, characterized by the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques and tau tangles that disrupt neural communication. After treatment, these mice exhibited a significant reduction in plaque buildup and improved performance on memory-related tasks, such as navigating mazes. Lead researcher Hans Christian Cederberg Helms noted that arginine enhances the brain’s natural waste-clearing mechanisms, potentially flushing out toxic proteins before they can accumulate.
Affordable Solutions in Drug Development
Repurposed medications like arginine could expedite the development of therapies for Alzheimer’s. Unlike new drugs, which can cost billions and take years to develop, arginine already has a well-established safety profile, having been approved for conditions such as hypertension. This makes it an attractive option for pharmaceutical companies facing challenges with patent expiration and rising research and development costs. Industry experts suggest that repurposing drugs could dramatically cut expenses and expedite the path to human therapies.
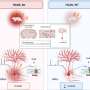
In examining the mechanisms behind arginine’s effects, the research highlighted the amino acid’s influence on the glymphatic system, which acts as the brain’s waste removal system. In Alzheimer’s patients, this system often falters, leading to harmful accumulations of debris. The Copenhagen study found that arginine enhances fluid flow through this system, effectively “washing” the brain clean. Mice treated daily for several weeks not only had fewer plaques but also displayed behavioral improvements, such as enhanced social recognition and reduced anxiety-like symptoms, mirroring human cognitive decline.
Despite these promising results, experts caution that findings from mouse models do not always translate to humans. Previous anti-amyloid drugs that successfully cleared plaques failed to halt cognitive decline, highlighting the significant gap that exists between animal studies and human experiences. Nevertheless, the low risk of arginine makes it a prime candidate for expedited human trials, potentially commencing within the next year.
Innovations in Nanotechnology and Cancer Drug Repurposing
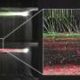
Recent advancements in nanotechnology have also shown great promise in combating Alzheimer’s. Research teams in Spain and China have developed nanoparticles capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier, a significant challenge for many therapeutic agents. According to a report featured in Medical News Today, these nanoparticles have reduced plaque levels by 50-60% in treated mice, leading to memory recovery in behavioral tests. The approach utilizes magnetic nanoparticles that carry peptides designed to bind and dissolve toxic aggregates.
In parallel, the intersection of oncology and neurology has led to unexpected breakthroughs. A study highlighted in ScienceAlert explored how cancer drugs like letrozole and irinotecan not only diminished plaques but also improved motor skills and learning abilities in mice. These drugs, already well-tolerated in humans, bring decades of safety data from cancer treatments, adding to the appeal of repurposing them for Alzheimer’s therapy.
While some repurposing efforts have encountered setbacks—such as Novo Nordisk’s trials of GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide failing to show benefits against Alzheimer’s—the overall momentum in 2025 suggests a growing optimism within the field. Social media platforms have amplified discussions around these developments, with researchers sharing promising results about rapid plaque clearance via nanoparticles and other innovative therapies.
The potential of vaccines also remains a focus for researchers. The Mayo Clinic is currently investigating vaccines that stimulate immune responses against amyloid-beta, with early mouse studies indicating that vaccinated subjects maintain cognitive function longer than controls. Such advancements align with a broader therapeutic shift, as detailed in a Scientific American overview.
As the field of Alzheimer’s research evolves, the combination of repurposed drugs, nanotechnology, and vaccines presents a multi-faceted approach to combating this complex disease. Experts emphasize the need for integrated strategies that address plaques, inflammation, and vascular health simultaneously. While challenges persist regarding the translation of findings from mice to humans, the significant increase in promising results signals a potential turning point in developing effective treatments for Alzheimer’s.
Repurposed drugs like arginine exemplify how revisiting established medications can yield new hope in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases. With ongoing research and collaboration, the prospect of viable therapies for preserving cognitive function and enhancing the quality of life for Alzheimer’s patients may soon become a reality.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBreakthroughs and Challenges Await Science in 2026
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoTop 10 Penny Stocks to Watch in 2026 for Strong Returns
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoJapanese Study Finds Rose Oil Can Increase Brain Gray Matter
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Education6 months ago
Education6 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications