Science
New AI Model Boosts Wheat Spike Counting Accuracy Above 95%
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences have developed an advanced deep learning model that enhances the accuracy of wheat spike counting, achieving precision levels exceeding 95%. This breakthrough, detailed in a study published on May 13, 2025, in the journal Plant Phenomics, is crucial for addressing the challenge of increasing global wheat production to meet the demands of a growing population.
Wheat serves as a fundamental component of diets for billions worldwide, providing essential carbohydrates, proteins, and dietary fiber. With projections indicating that wheat production must rise by at least 60% by 2050 to sustain future food needs, traditional breeding techniques have primarily focused on kernel size and quantity. However, progress in improving spike number (SN)—a key trait influenced by genetics, planting density, and management practices—has lagged behind.
Manual counting of spikes in the field is not only time-consuming but also subjective, making it impractical for large-scale agricultural trials. Although advancements in computer vision and deep learning have facilitated automated detection of plant traits, achieving accuracy under real-world conditions remains a challenge, particularly when dealing with dense and overlapping spikes.
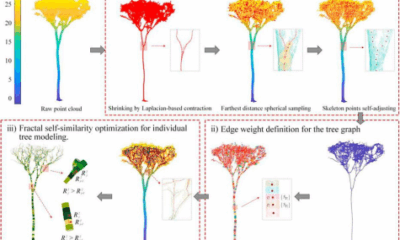
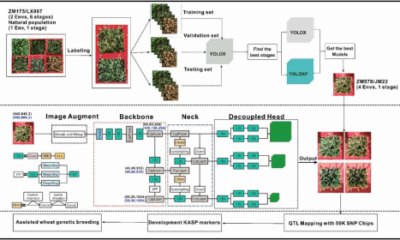
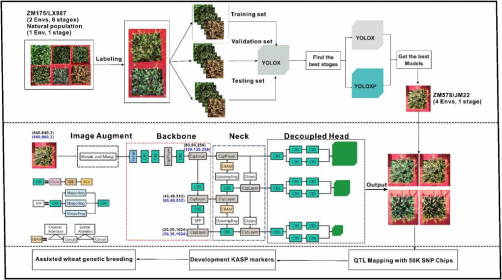
To overcome these obstacles, the research team optimized their methodology by applying next-generation algorithms to refine spike counting and correlate phenotypic data with genetic markers. The study utilized images collected during six growth stages of the Zhongmai 175 × Lunxuan 987 recombinant inbred line (RIL) population, subsequently validating the findings in additional populations.
The team trained ten models and assessed their performance using four indices: precision, recall, mean average precision (mAP), and F1 score. The results demonstrated consistently high precision rates ranging from 88.19% to 95.48%, indicating reliable spike identification. However, recall rates varied considerably, from 44.60% to 81.23%. Notably, the late grain-filling (LGF) stage delivered optimal performance, achieving the highest recall of 81.23% and mAP values between 85.69% and 89.47%.
The study also highlighted the significance of annotation quality in determining accuracy. The smallest discrepancy between manual and automated counts was noted during the LGF stage. Strong correlations (r = 0.84–0.88) were observed between manual and model counts, particularly in models trained in Dezhou and tested in Changping.
In a significant advancement, the researchers enhanced the YOLOX-P algorithm by incorporating attention modules and utilizing higher-resolution input images. This modification led to a remarkable improvement in performance, increasing mAP by 5.30–5.99% and raising F1 scores by 0.06 compared to the original YOLOX model. Among various integrated datasets, the CD&DD subset trained with YOLOX-P achieved the highest mAP of 91.81%.
Further validation in the Zhongmai 578 × Jimai 22 population confirmed the robustness of these models, with correlation coefficients ranging from 0.73 to 0.82 between automated and manual counts. Genetic analysis revealed four stable quantitative trait loci (QTLs)—QSN.caas-4A2, QSN.caas-4D, QSN.caas-5B1, and QSN.caas-5B2—linked to spike number. The team also developed Kompetitive allele-specific PCR markers for two loci, providing essential tools for marker-assisted breeding.
This integration of artificial intelligence with plant genetics represents a significant advancement in wheat breeding. The automated spike counting process lessens the reliance on labor-intensive field assessments, accelerates phenotyping, and offers objective, scalable data for breeding programs. The validated genetic markers equip breeders with immediate tools to select varieties with higher spike numbers, which is essential for enhancing yield.
The findings from this research hold promise for improving wheat productivity, ultimately contributing to global food security in the face of rising population demands.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods