Science
Hubble Discovers Betelgeuse’s Hidden Companion Star in Stellar Wake
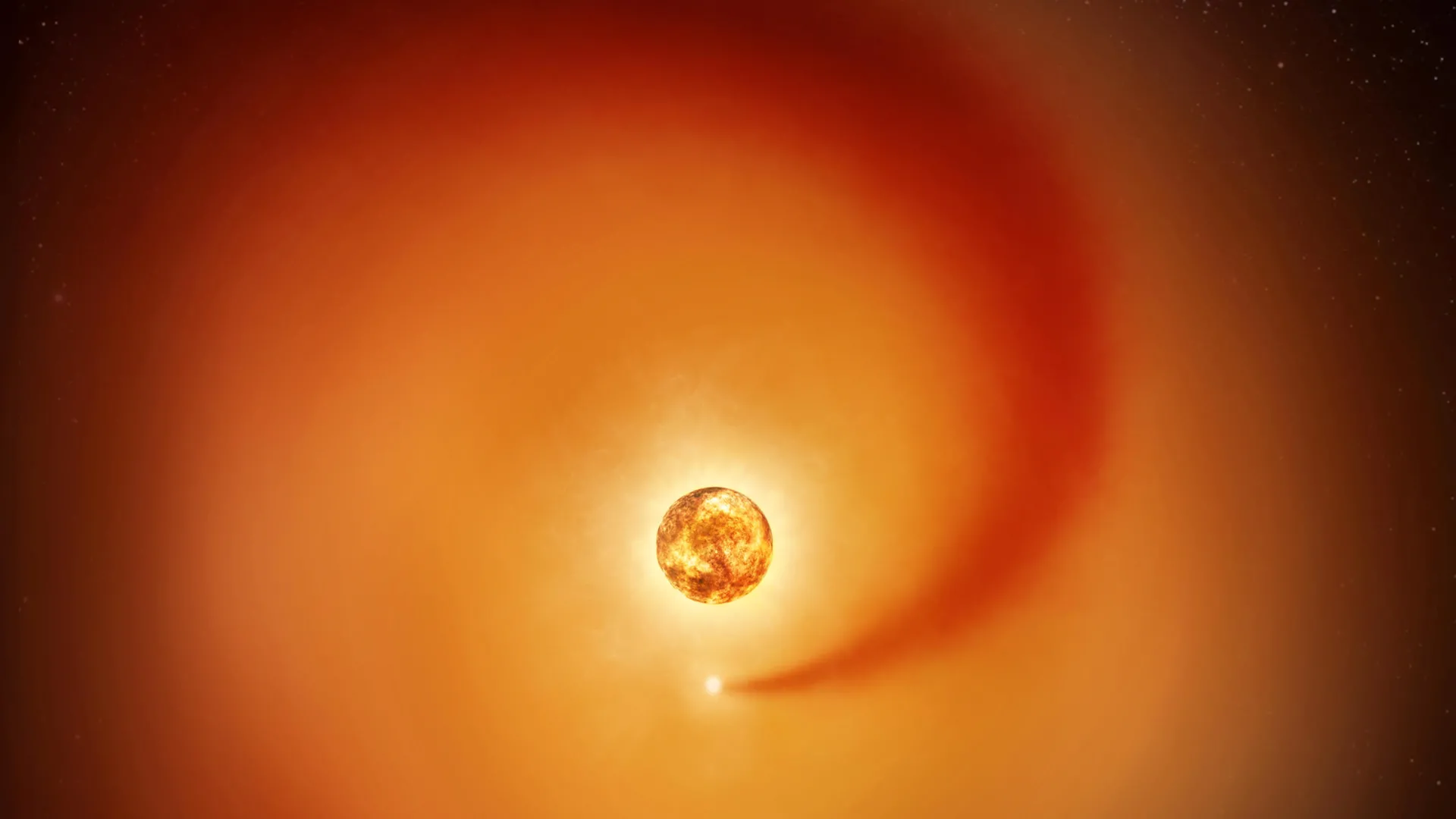
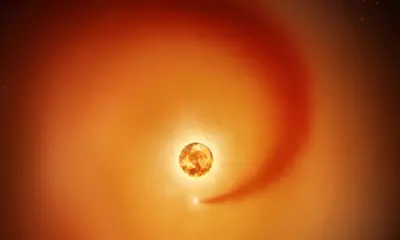
Astronomers have confirmed the existence of a companion star orbiting the red supergiant Betelgeuse, revealing significant insights into its unusual behavior. Using nearly eight years of observations from the NASA Hubble Space Telescope and various ground-based observatories, scientists identified a small star, named Siwarha, that is creating a visible wake as it moves through Betelgeuse’s outer atmosphere. This discovery sheds light on the long-standing enigma surrounding Betelgeuse’s variability.
The findings were presented at a recent news conference during the 247th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Phoenix and have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. The research, conducted by a team at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, marks a significant milestone in understanding how massive stars like Betelgeuse evolve.
Unraveling the Secrets of Betelgeuse
Researchers detected the influence of Siwarha by meticulously analyzing fluctuations in Betelgeuse’s light over nearly eight years. These observations provided evidence of the companion star’s impact on the giant star’s atmosphere. As Siwarha traverses Betelgeuse’s outer layers, it disrupts the surrounding gas, leaving behind a trail of dense material. This revelation offers an explanation for the star’s erratic brightness and atmospheric behavior.
Betelgeuse is located approximately 650 light-years from Earth in the Orion constellation. The star is a red supergiant, vast enough to contain more than 400 million Suns, making it one of the few stars whose surface and atmosphere can be studied in detail. Understanding Betelgeuse’s life cycle is crucial for astronomers studying massive stars, as it provides a window into the processes leading to supernova explosions.
The team combined Hubble data with observations from the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory and the Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory to uncover patterns in Betelgeuse’s behavior. They observed shifts in the star’s spectrum and changes in the motion of gas in its outer atmosphere, confirming the presence of the companion star. The wake produced by Siwarha appears approximately every 2,100 days, coinciding with earlier theoretical predictions.
Clarifying Betelgeuse’s Variability
For decades, astronomers have monitored Betelgeuse, attempting to explain its unpredictable brightness fluctuations. Interest peaked in 2020 when the star unexpectedly dimmed after what was dubbed a stellar “sneeze.” Researchers had identified two primary cycles in Betelgeuse’s variability: a shorter 400-day cycle associated with pulsations within the star and a longer cycle lasting about 2,100 days.
Prior to this discovery, multiple theories were proposed to explain Betelgeuse’s long-term behavior, including massive convection cells, dust clouds, magnetic activity, and the possibility of a hidden companion star. Although previous studies hinted at a low-mass star within Betelgeuse’s atmosphere, conclusive evidence was lacking until now. The newly detected wake provides the strongest proof yet that a companion star is influencing Betelgeuse’s atmosphere.
Andrea Dupree, an astronomer at the CfA and lead author of the study, remarked, “The idea that Betelgeuse had an undetected companion has been gaining popularity for the past several years, but without direct evidence, it was an unproven theory. With this new direct evidence, Betelgeuse gives us a front-row seat to watch how a giant star changes over time.”
Looking ahead, astronomers plan to conduct additional observations of Siwarha when it becomes visible again in 2027. This discovery not only enhances understanding of Betelgeuse but may also aid in solving similar mysteries involving other massive stars.
The Hubble Space Telescope, operational for over 30 years, continues to make significant contributions to our understanding of the universe. Managed collaboratively by NASA and the European Space Agency, Hubble remains a vital tool for astronomers worldwide, uncovering the secrets of celestial phenomena.
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Education4 months ago
Education4 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts