Science
Cleveland Researchers Identify Enzyme for Potential Obesity Drug
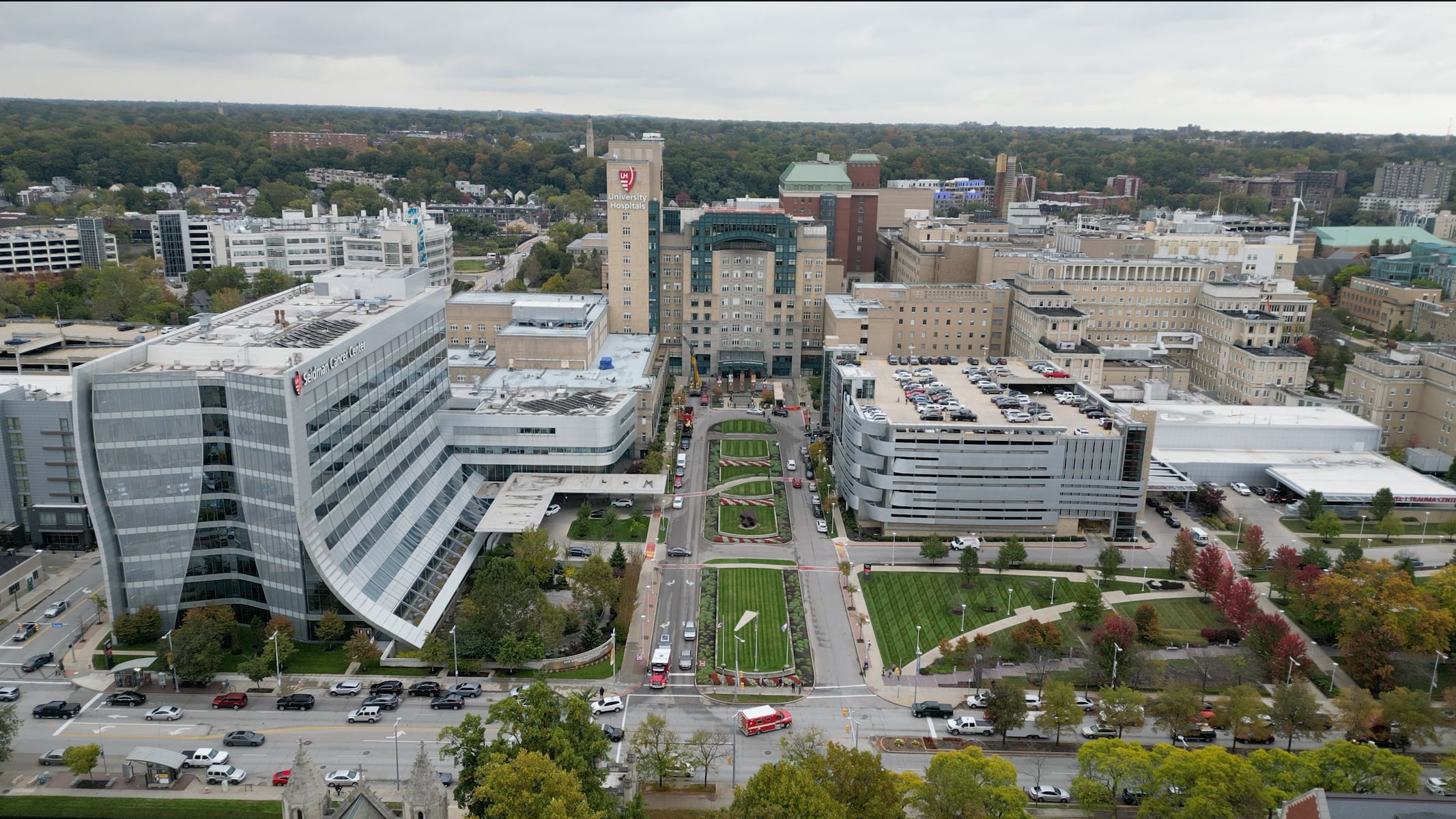

Researchers at University Hospitals and Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland have made a significant breakthrough in obesity treatment. They have identified an enzyme known as SCoR2, which plays a crucial role in fat production. This discovery could pave the way for a three-in-one drug targeting obesity, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease.
The research team found that SCoR2 removes nitric oxide from proteins that regulate fat accumulation in the body. In experiments involving mice, blocking this enzyme resulted in no weight gain, lower cholesterol levels, and reduced liver injury. Dr. Jonathan Stamler, lead author of the study and president of the Harrington Discovery Institute, emphasized the potential impact of this research, stating, “We have a new class of drug that prevents weight gain and lowers cholesterol—a potential therapy for obesity and cardiovascular disease, with additional hepatic benefits.”
Understanding the Role of Nitric Oxide
Published in the journal Science Signaling, the study reveals how nitric oxide functions as a regulatory mechanism on fat production. In the liver, it inhibits the proteins responsible for synthesizing fat and cholesterol. Furthermore, in adipose tissue, nitric oxide blocks the genetic pathways that lead to the formation of fat-producing enzymes. The action of SCoR2, which removes nitric oxide, effectively activates fat synthesis, underscoring the enzyme’s necessity in fat production.
The researchers validated their findings by using both genetic and pharmaceutical methods to inhibit SCoR2. This dual approach demonstrated consistent results, reinforcing the enzyme’s role in regulating body fat.
Next Steps in Drug Development
Looking ahead, the research team plans to advance their findings into clinical trials within approximately 18 months. The Harrington Discovery Institute will assist in developing what Dr. Stamler describes as a “first-in-class drug” that may also confer beneficial effects on liver health. The institute has a robust portfolio, featuring 227 medicines in development, including 24 medicines currently in clinical trials and 46 companies launched since its inception 13 years ago.
This research represents a promising advancement in the quest to address significant health issues related to obesity and its associated conditions. The potential for a multi-faceted treatment could have far-reaching implications for public health and patient care.
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions