Technology
Nanolasers Set to Transform Optical Computing and Quantum Security
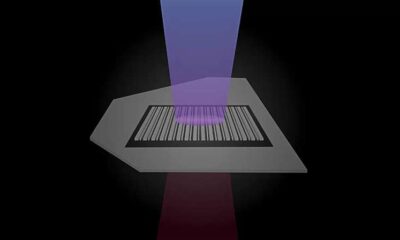
Recent advancements in the field of nanophotonics have highlighted the potential of nanolasers as pivotal components for next-generation technologies. These tiny lasers, which utilize light to process information, are increasingly recognized for their applications in high-speed optical computing, quantum cryptographic communication, and ultra-high-resolution augmented reality (AR) displays.
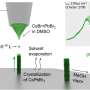
The growing interest in nanolasers stems from their ability to operate at scales smaller than traditional lasers while maintaining high efficiency. Researchers are exploring new methods for the direct 3D printing of these devices, a development that could significantly streamline the manufacturing process. According to a study published in the journal *Nature Photonics*, the direct printing technique allows for precise control over the nanolaser’s properties, providing a pathway for mass production that could drive down costs and enhance performance.
Impact on High-Tech Industries
The implications of this technology extend across several high-tech sectors. For instance, in the realm of artificial intelligence, optical computing powered by nanolasers could lead to processing speeds far exceeding those of current electronic systems. Such advancements could facilitate the development of more sophisticated AI models, capable of analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time.
Moreover, quantum cryptographic communication is poised for a revolution with the integration of nanolasers. Their ability to generate and manipulate photons could enhance the security of data transmission, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to intercept sensitive information. This aspect is particularly crucial in times when data privacy is a growing concern for individuals and organizations alike.
In addition, the potential application of nanolasers in augmented reality (AR) displays offers a glimpse into the future of immersive technologies. With their capability to produce light at extremely small scales, nanolasers could contribute to the creation of ultra-high-resolution displays that provide more realistic and engaging user experiences.
Future Prospects and Challenges
While the prospects for nanolasers are promising, several challenges remain. The scalability of 3D printing techniques needs to be validated through further research, ensuring that these devices can be produced efficiently and economically. Additionally, integrating nanolasers into existing semiconductor technologies will require collaboration among various sectors, including materials science and engineering.
Experts from institutions such as the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Stanford University are actively working on overcoming these hurdles. Their collective efforts could pave the way for commercial applications of nanolasers in the near future, potentially transforming industries ranging from telecommunications to healthcare.
In conclusion, the direct 3D printing of nanolasers holds significant promise for the advancement of optical computing and quantum security. As researchers continue to explore this innovative technology, its impact on high-tech industries is expected to grow, ushering in a new era of light-based information processing.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoBreakthroughs and Challenges Await Science in 2026
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology8 months ago
Technology8 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoTop 10 Penny Stocks to Watch in 2026 for Strong Returns
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoJapanese Study Finds Rose Oil Can Increase Brain Gray Matter
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Education6 months ago
Education6 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications