Science
Study Reveals Space Travel Accelerates Aging in Blood Stem Cells
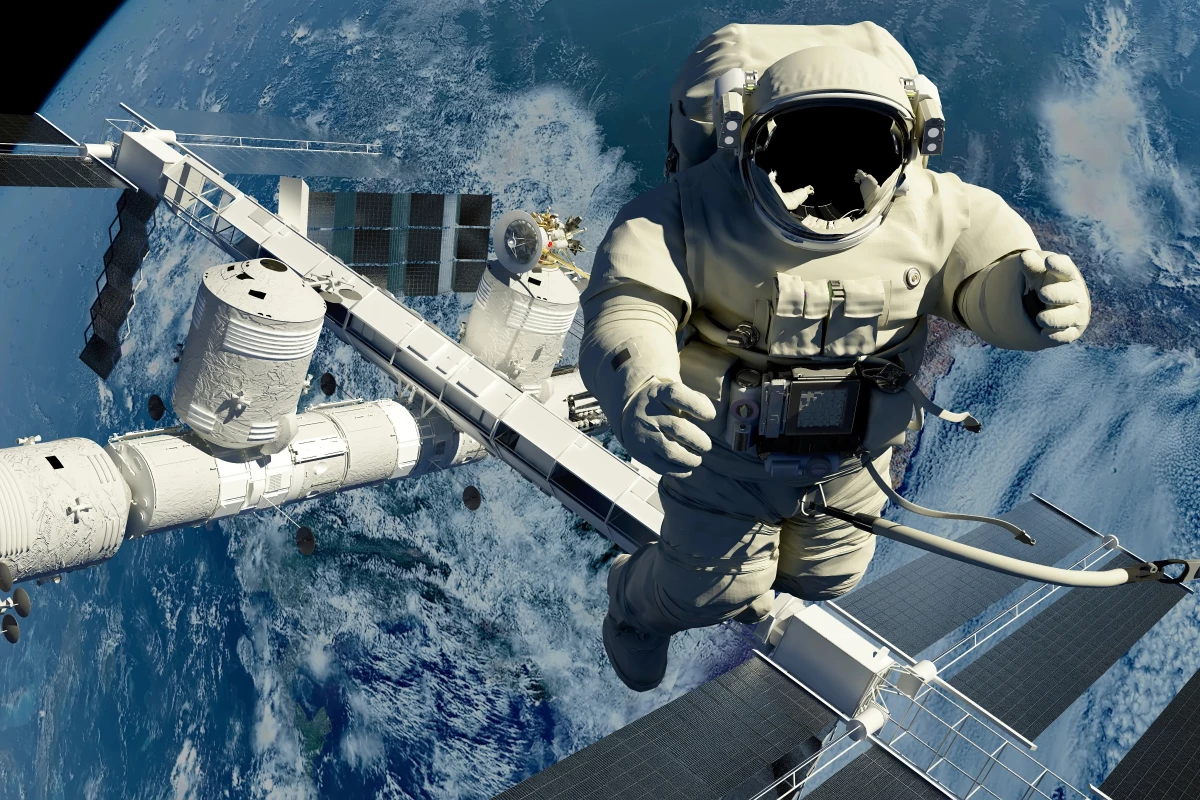

Recent research indicates that space travel accelerates aging in blood-forming stem cells, also known as hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). A collaborative study involving the University of California, San Diego’s Sanford Stem Cell Institute, NASA, and Space Tango examined the effects of the low gravity and radiation found in low Earth orbit (LEO) on these vital cells. The findings suggest that exposure to space conditions can significantly impact the health and longevity of HSCs.
To investigate this phenomenon, researchers established the Integrated Space Stem Cell Orbital Research (ISSCOR) center. Over four missions with SpaceX’s Commercial Resupply Services, they monitored HSCs before, during, and after flights to the International Space Station (ISS). This research employed innovative bone marrow niche nanobioreactors, which allowed real-time tracking of HSCs within artificial intelligence-driven CubeLabs.
The study revealed that HSCs returning from space exhibited considerable signs of wear. These cells showed a diminished capacity to produce healthy new cells, increased vulnerability to DNA damage, and signs of telomere fraying—telomeres being the protective caps on the ends of chromosomes. Collectively, these changes suggest that the cells age more rapidly in the harsh environment of space.
Catriona Jamieson, director of the Sanford Stem Cell Institute and professor of medicine at UC San Diego School of Medicine, described space as “the ultimate stress test for the human body.” She emphasized the implications of the study for both astronaut health during long-duration missions and for understanding human aging and diseases, such as cancer, on Earth. “Understanding these changes not only informs how we protect astronauts during long-duration missions but also helps us model human aging and diseases like cancer here on Earth,” noted Jamieson.
Building upon insights from NASA’s Twins Study, the research conducted at ISSCOR provided a detailed exploration of the mechanisms behind space-induced molecular aging. After just 32 to 45 days in space, HSCs began exhibiting signs of premature aging, becoming hyperactive and depleting their energy reserves. This loss of regenerative capacity poses risks for long-term health, as the cells struggled to maintain their function and stability.
The study identified genotoxic stress from increased exposure to cosmic radiation as a significant factor contributing to stem cell aging in space. During the missions, NASA recorded radiation levels between 7.6 and 10.7 milligray (mGy), comparable to the exposure from routine medical scans such as CT or X-rays. While these doses may seem moderate, even minimal exposure to cosmic radiation can cause cellular damage, especially when combined with other stress factors present in space.
Interestingly, when the space-exposed HSCs were returned to a healthy environment on Earth, some signs of damage began to heal. This suggests that, under the right conditions, aging cells may recover, akin to astronauts returning from their missions. The findings underscore the urgent need for strategies to shield stem cells from the detrimental effects of space.
The research team is now looking to expand their studies. They plan to conduct further missions to the ISS, incorporating astronauts to track molecular changes in real time. Their objectives include exploring pharmaceutical or genetic tools that could mitigate the health risks posed by space travel.
The new study, published in Cell Stem Cell, marks a significant advancement in understanding the intersection of space travel and cellular aging. As commercial space travel becomes increasingly viable, these insights will be crucial in ensuring the health and safety of astronauts and, by extension, enhancing our understanding of human biology.
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoDiscover the Best Wireless Earbuds for Every Lifestyle