Science
Scientists Uncover Evidence of Ice Ages on Mars Through Space Imaging
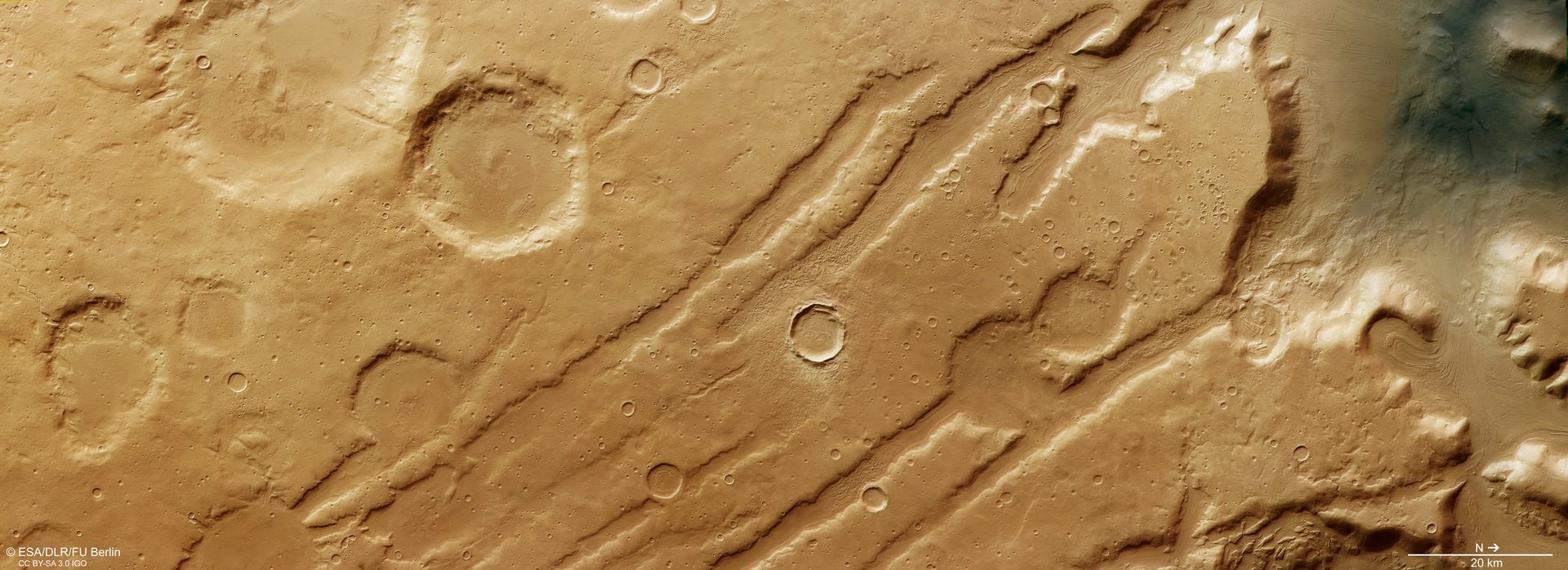

Recent findings have revealed that Mars has undergone multiple ice ages, mirroring Earth’s climatic history. Using advanced imaging technology, scientists have captured detailed images of features on Mars that indicate past glacial activity. This research, conducted by the European Space Agency’s ESA with the High Resolution Stereo Camera on the Mars Express orbit, highlights the planet’s complex environmental changes over millions of years.
The images focus on a significant area known as Coloe Fossae, a system of intersecting canyons located in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. These canyons reveal intricate patterns, known as lineated valley fill (LVF) and concentric crater fill (CCF), which suggest the movement of ice across the Martian surface during past ice ages. The distinctive swirling lines visible in the canyons indicate where glacial materials flowed, similar to formations found on Earth.
Earth’s history includes well-documented ice ages, particularly during the Pleistocene epoch, which lasted from approximately 2.58 million to 11,700 years ago. During this time, average global temperatures were around 8 °C (14.5 °F) cooler than today. Indigenous cultures have preserved oral histories that describe significant climate shifts, providing a rich context for understanding these environmental transformations. This aligns with geological evidence showing that Earth has experienced several ice ages over the past 2.5 billion years.
Mars experiences similar climatic shifts primarily due to variations in its axial tilt, known as obliquity. These changes in tilt lead to fluctuations in temperature, causing ice flows to advance and retreat across the planet’s surface. The evidence gathered from the Mars Express images indicates that glaciers once extended from the Martian poles toward mid-latitude regions before retreating during warmer interglacial periods.
The LVF and CCF patterns observed in the Coloe Fossae area signify that Mars previously hosted glaciers far from its polar ice caps. This discovery supports the notion that the planet underwent extensive glacial activity, a fact that has implications for our understanding of Mars’ environmental history. As scientists study these features, they gain insights into how Mars transitioned from a warmer, wetter planet to the cold and arid environment observed today.
Tracking the flow of ice on Mars is crucial for reconstructing the planet’s geological and environmental timeline. This research not only enhances our understanding of Mars but also provides valuable context for Earth’s own climatic history. The ongoing exploration of planetary ice ages offers a fascinating perspective on how celestial bodies evolve over time.
For those interested in delving deeper into this research, an annotated version of the images is available, providing closer looks at the LVF features identified on Mars. The findings from ESA’s Mars Express continue to shed light on the planet’s past, offering tantalizing clues about its climatic changes and potential for past life.
Further Reading: ESA
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoDiscover the Best Wireless Earbuds for Every Lifestyle