Science
Researchers Unveil New Method to Control Heat Flow Using Magnons
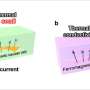
A collaborative research team from the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), the University of Tokyo, the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), the University of Osaka, and Tohoku University has introduced an innovative approach to actively manage heat flow in solid materials. This method leverages the transport of magnons, which are quasiparticles that represent the collective motion of spins in magnetic materials.
The researchers have shown that magnons play a more significant role in heat conduction within a ferromagnetic metal and its junction than previously understood. This breakthrough could have profound implications for thermal management in various technological applications, including data storage and electronic devices.
Understanding Magnons and Their Impact
Magnons, as quasiparticles, have attracted considerable attention in the field of condensed matter physics. Their ability to convey energy through magnetic materials opens new avenues for controlling thermal properties. The team’s research demonstrates that by manipulating magnons, it is possible to enhance or inhibit heat flow in solids, a capability that could lead to the development of more efficient thermal management systems.
The study reveals that magnons contribute significantly to the heat conduction process in ferromagnetic materials, providing insights that could reshape the understanding of thermal transport in such systems. The findings suggest that this form of energy transport could be harnessed for practical applications, potentially improving the performance of devices that rely on precise temperature control.
Implications for Future Technology
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest. As electronic devices continue to become smaller and more powerful, effective heat dissipation becomes increasingly critical. The ability to control heat flow using magnon transport can lead to improved thermal efficiency in a variety of applications, from computer chips to power electronics.
Furthermore, this research aligns with the growing interest in spintronics, a field that utilizes the intrinsic spin of electrons for information processing. By integrating magnon-based thermal control into spintronic devices, researchers may unlock new functionalities that could revolutionize data processing and storage technologies.
As the team continues to explore the potential of their findings, the scientific community eagerly anticipates further developments in this exciting area of research. The innovative method of controlling heat flow through magnons not only enhances fundamental understanding but also paves the way for future advancements in material science and technology.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2





















