Science
Researchers Uncover Factors Driving Microplastics’ Environmental Impact
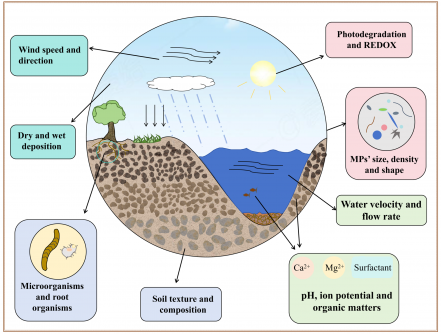
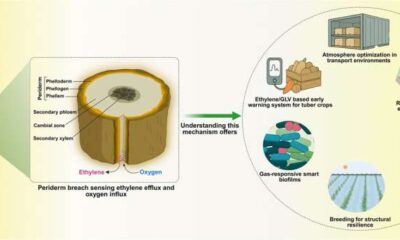
Microplastics (MPs), defined as plastic particles less than 5 mm in diameter, are increasingly recognized as pervasive pollutants in various ecosystems. A recent review by researchers, including Feifei Feng and Wenqi Ye from the Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, seeks to clarify the factors influencing the migration and distribution of these microplastics. This comprehensive study was published in the journal Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in 2025.
The research highlights the extensive presence of microplastics across aquatic, terrestrial, and atmospheric environments. Classified by their chemical makeup, size, and origin, these pollutants pose significant risks to both ecosystems and human health. The review addresses critical issues such as bioaccumulation, composite pollution, and cross-media migration of microplastics, although the mechanisms behind these processes remain poorly understood.
Key Drivers of Microplastics Behavior
The authors systematically summarized the intrinsic properties of microplastics and various environmental factors that influence their behavior. Key characteristics of microplastics, such as size, shape, and aging state, play a crucial role in determining their ecological interactions. Environmental conditions, including hydrological parameters, soil texture, meteorological aspects, and biological interactions with microorganisms and root organisms, also significantly affect how microplastics migrate through different media.
This interconnected analysis reveals that the behavior of microplastics is driven by a complex interplay of factors. These influences dictate transport pathways, retention hotspots, and the long-term ecological implications of microplastic contamination.
Framework for Addressing Microplastics
A noteworthy outcome of this review is the establishment of a unified framework for understanding the environmental interactions of microplastics. The researchers propose several regulatory strategies aimed at mitigating the impact of these pollutants. Suggested approaches include source control measures, such as banning primary microplastics and developing biodegradable alternatives, alongside process interruptions through the use of constructed wetlands, biochar, and plant shelterbelts.
The findings from this review provide a significant contribution to the ongoing discourse on environmental pollution and offer actionable insights for policymakers and environmental scientists alike. For a more detailed examination of the study, the full paper is accessible at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-025-2062-z.
This research marks a crucial step towards understanding microplastics, fostering informed strategies to combat their pervasive presence in the environment.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBreakthroughs and Challenges Await Science in 2026
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology8 months ago
Technology8 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoTop 10 Penny Stocks to Watch in 2026 for Strong Returns
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoJapanese Study Finds Rose Oil Can Increase Brain Gray Matter
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Education6 months ago
Education6 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications