Science
Researchers Explore Light-Based AI to Combat Energy Demands

The escalating energy consumption of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has sparked significant concern among researchers and industry leaders. As AI systems like Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) and large language models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated across various sectors, their reliance on energy-intensive hardware such as graphics processing units (GPUs) has come under scrutiny. To address these challenges, Professor Ajay Joshi of Boston University is spearheading efforts to develop innovative computing architectures that could potentially outperform traditional electronic systems while reducing energy consumption.
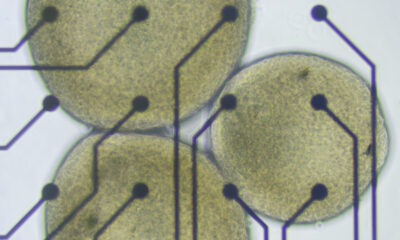
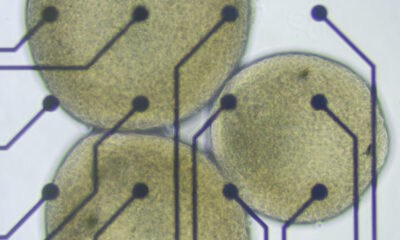
Supported by a substantial $1.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF), Professor Joshi is focusing on the project titled ASCENT: Heterogeneously Integrated Electronic Photonic AI Accelerators (HIEPAA). This initiative aims to leverage light-based computing technologies to create more energy-efficient AI hardware. Light offers a more efficient medium for data transmission compared to electricity, making it a promising alternative in the quest for sustainable computing solutions.
Recent advancements in integrated electronic-photonic systems have highlighted the potential of this approach. Professor Joshi’s research incorporates an electro-optical metamaterial known as thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) into silicon photonic chip platforms. This integration is designed to produce analog optical modulators, which can significantly enhance computing speeds while minimizing data loss compared to conventional silicon-based devices.
In pursuit of these goals, Joshi plans to design new architectures and circuit techniques aimed at achieving efficient and highly accurate AI computations using low-precision building blocks. This concept builds on previous research conducted by his team, which was published in Nature Communications. By focusing on these innovations, the project aligns with broader efforts to develop sustainable AI technologies that meet the demands of an increasingly digital world.
Professor Joshi leads the Integrated Circuits, Architectures, and Systems Group at Boston University and has received numerous accolades for his work, including multiple Google Faculty Research Awards and a 2012 NSF CAREER AWARD. He also serves as the CEO and co-founder of CipherSonic Labs, a start-up dedicated to advancing data privacy technologies. In recognition of his contributions, he received the 2024 BU Technology Development Ignition Award.
The research led by Professor Joshi is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of AI, offering a pathway to more sustainable technology solutions that could alleviate the environmental impact of the tech industry. As the demand for AI continues to soar, innovations like those being explored in this project may prove crucial in balancing technological advancement with ecological responsibility.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods