Science
NUS Researchers Innovate Sustainable Nitrogen Insertion Method
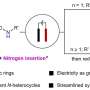
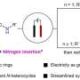
Researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have unveiled a groundbreaking electrochemical reaction system that facilitates the efficient insertion of nitrogen atoms into saturated carbocycles. This innovative method paves the way for the synthesis of functionalized quinolines and N-alkylated saturated nitrogen heterocycles, both of which are vital frameworks in synthetic chemistry and pharmaceutical applications.
The research team has developed a manifold that optimizes the electrochemical process, enabling more sustainable practices in chemical synthesis. Traditional methods of nitrogen insertion often rely on hazardous reagents and high energy inputs, making this new approach significantly more environmentally friendly. By using electricity to drive the reaction, the NUS team has reduced the reliance on toxic materials typically involved in the synthesis of nitrogen-containing compounds.
Emerging details reveal that this novel reaction not only enhances the efficiency of nitrogen insertion but also expands the versatility of the resulting compounds. Quinolines, for instance, are essential in the development of various pharmaceuticals, including treatments for malaria and other diseases. The ability to functionalize these compounds opens new avenues for medicinal chemistry.
The significance of this advancement is underscored by its potential applications. The method could contribute to more efficient drug development processes, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable practices in the pharmaceutical industry. The ability to produce complex nitrogen-containing structures in a more environmentally conscious manner could facilitate breakthroughs in the development of new therapies.
This work represents a significant step forward in the field of synthetic chemistry, highlighting the importance of integrating sustainability into chemical processes. The findings from this research are expected to spur further studies and innovations aimed at improving the efficiency and safety of chemical synthesis on a global scale.
The research was published in a reputable scientific journal, emphasizing the credibility and impact of the findings. As the world increasingly prioritizes sustainability, the implications of this research resonate across various sectors, particularly in healthcare and pharmaceuticals. The NUS team’s dedication to advancing eco-friendly methodologies in chemistry reflects a broader trend towards responsible scientific practices.
In conclusion, the development of this electrochemical reaction manifold for nitrogen insertion marks a pivotal moment in synthetic chemistry, with far-reaching implications for the pharmaceutical industry and beyond. The NUS researchers have not only contributed to scientific knowledge but also set a benchmark for future innovations that prioritize environmental sustainability.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods