Science
Experience the Spectacular Geminid Meteor Shower This December
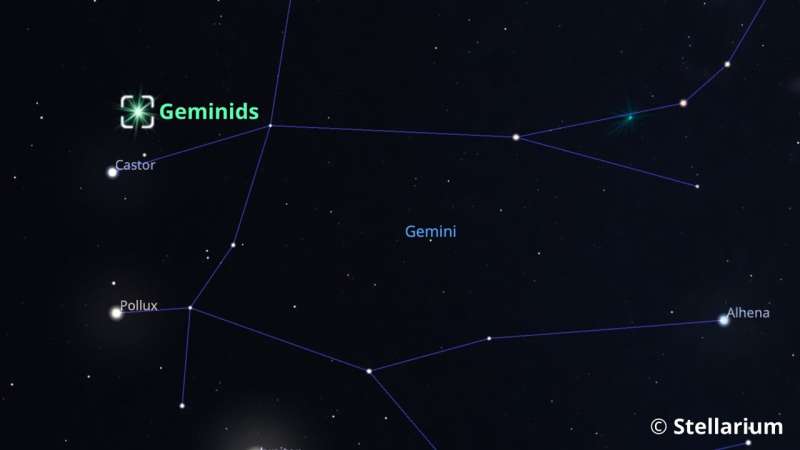
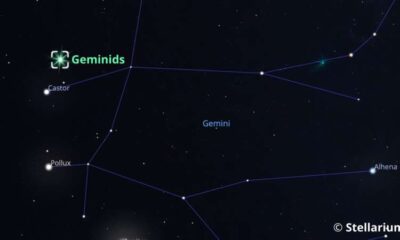
The annual Geminid meteor shower is set to peak this weekend, offering skywatchers a remarkable opportunity to witness up to 100 meteors per hour under ideal conditions. This celestial event is visible between now and December 20, 2025, with the highest activity expected overnight from December 13 to 14.
What Makes the Geminids Unique?
Unlike most meteor showers that originate from comets, the Geminids stem from the debris of an object known as 3200 Phaethon, which resembles an asteroid. This unusual origin contributes to the Geminids being one of the most reliable and vibrant meteor showers of the year.
In a video produced by the Royal Astronomical Society, Dr. Robert Massey, Deputy Executive Director, emphasizes the ease of observing the Geminids. He advises, “The naked eye is the best way to see them. Using a telescope or binoculars restricts your view, and with a meteor shower, you want the widest possible perspective.”
Dr. Massey elaborates that viewers should lie back and gaze at the broad expanse of stars, watching for short streaks of light that last about half a second. “You can expect to see perhaps up to 100 meteors an hour, which is a brilliant view,” he notes, highlighting the shower’s impressive intensity.
Optimal Viewing Conditions
To experience the full beauty of the Geminids, it is crucial to find a location away from light pollution. Dr. Massey recommends heading to the countryside or areas with minimal artificial light. A clear sky is essential; cloudy weather can significantly hinder visibility. If conditions are not favorable during the peak, the meteor shower will continue until December 20, although at a diminished rate.
The Geminids were first documented in 1862 and have been intensifying ever since, making them a significant event for astronomy enthusiasts. Unlike other meteor showers, these meteors exhibit a greenish hue as they burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere, a result of their chemical composition, which includes elements like oxygen, magnesium, and nickel.
Meteors are fragments of interplanetary debris that travel at high speeds, often exceeding 130,000 kilometers per hour. When they enter the Earth’s atmosphere, friction generates intense heat, causing the particles to glow and creating the visible streaks known as shooting stars.
While random meteors (sporadics) can be seen on any night, the Geminids occur when the Earth’s orbit intersects streams of debris left by 3200 Phaethon. During these encounters, a surge in meteor numbers is observed, leading to the spectacular showers that attract stargazers around the world.
Meteors during the Geminid shower can appear anywhere in the sky, but they radiate from a single point in the constellation of Gemini, which gives the shower its name. The slow-moving nature of these meteors, combined with their vibrant colors, adds to the allure of this annual astronomical event.
As the Geminid meteor shower approaches its peak, enthusiasts and casual observers alike are encouraged to prepare for a night of celestial wonder. With the right conditions, this year’s display promises to be a memorable experience.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2