Science
Epigenetic Insights Reveal High-Altitude Adaptation in Andes

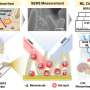
Research has identified a link between epigenetics and high-altitude adaptation among populations living in the Andes. Utilizing advanced DNA sequencing technology, scientists have explored how humans have evolved to thrive in diverse environments, particularly at elevations where oxygen levels are significantly lower.
A study focusing on the Andean population revealed that specific genetic adaptations have occurred to enhance their ability to utilize oxygen efficiently. This mirrors findings from research on Tibetans residing in the Himalayas, who possess a distinct variant of a gene that increases the oxygen-carrying capacity of their blood.
Understanding Genetic Adaptation at High Altitude
The study, conducted by a team of researchers, highlights the role of epigenetic changes in facilitating survival in extreme conditions. These changes can influence gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence, allowing populations to adapt to their surroundings over generations.
In the Andean region, where altitudes often exceed 3,000 meters, individuals demonstrate unique physiological traits. For instance, they have developed larger lung capacities and increased blood flow, which are crucial for maintaining adequate oxygen levels during physical exertion. This research underscores how environmental pressures can drive genetic evolution.
The implications of these findings extend beyond the Andes. Understanding how populations adapt could provide insights into health issues related to oxygen deprivation, such as those experienced by individuals living at lower altitudes or those suffering from respiratory conditions.
Broader Significance of Epigenetic Research
The use of DNA sequencing technology has opened new avenues for exploring human adaptation. This research not only sheds light on the genetic diversity within populations but also emphasizes how specific environmental challenges shape human biology.
As scientists continue to study these adaptations, it may lead to advancements in medicine and public health strategies. Enhanced knowledge of genetic variations related to altitude acclimatization could inform treatments for conditions like altitude sickness or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In conclusion, the connection between epigenetics and high-altitude adaptation in the Andes represents a significant step forward in understanding human resilience. As research in this field progresses, it may yield valuable insights into the ways our bodies respond to extreme environments, ultimately contributing to healthier populations worldwide.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide