Lifestyle
Bananas and Plantains: Key Differences Unveiled for Food Lovers
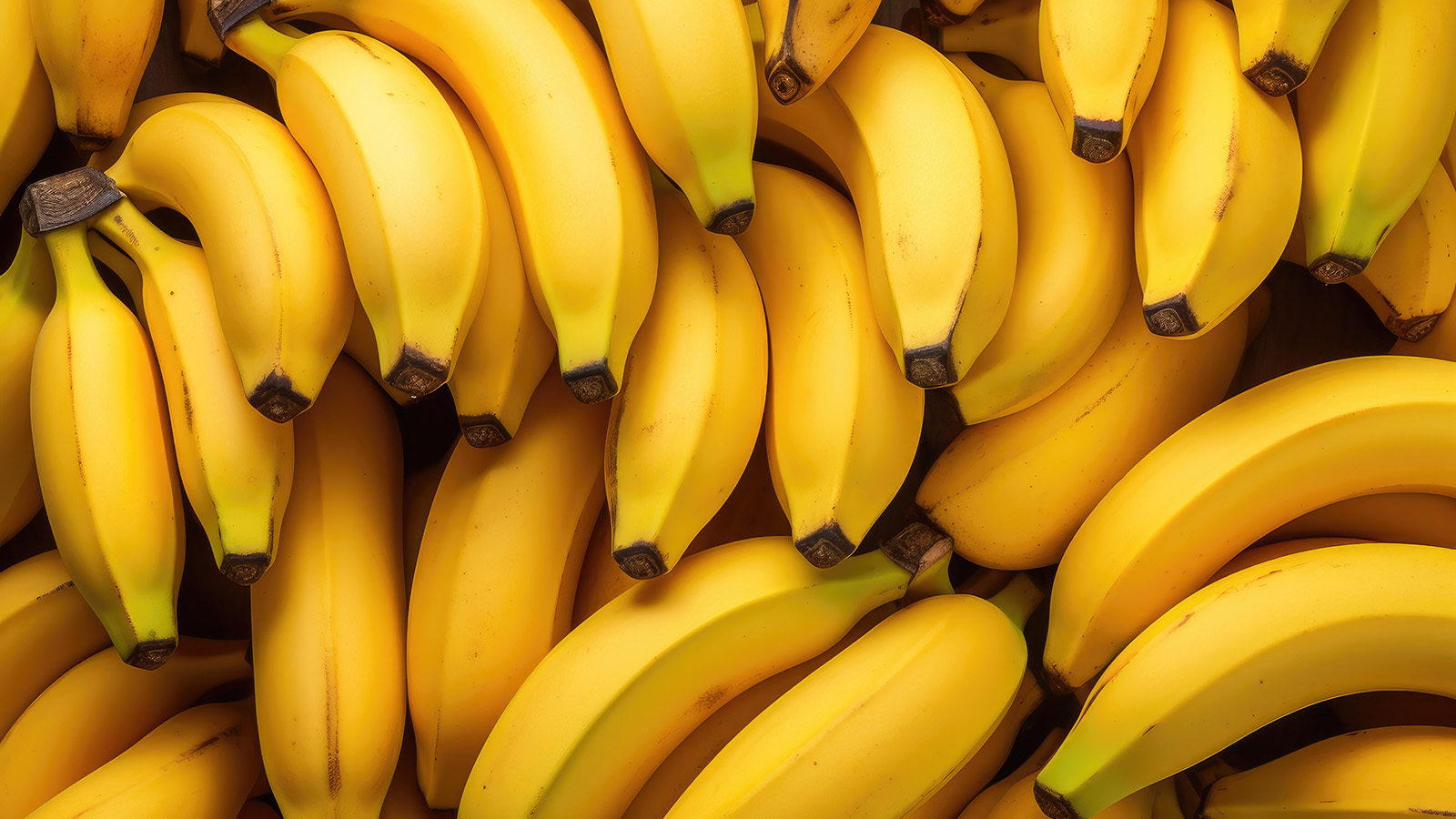

Bananas and plantains, both belonging to the genus Musa, differ significantly beyond their appearance. While these fruits thrive in tropical regions such as Southeast Asia, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean, their culinary applications and nutritional profiles set them apart.
Bananas are typically recognized for their bright yellow color, slender shape, and smooth skin. In contrast, plantains possess a thicker skin and a bulkier structure. This robust exterior makes plantains more challenging to peel, especially when they are still green. Ripe bananas are sweet and soft, commonly enjoyed raw or used in dishes like banana bread. Conversely, ripe plantains, which transition to yellow or dark brown, have a starchier flavor profile. Green plantains, on the other hand, are firm and are often featured in savory recipes that require frying or boiling.
In culinary terms, the two fruits serve different purposes. Bananas are primarily consumed raw, thanks to their inherent sweetness, making them a popular choice for smoothies, breakfast bowls, and baking. Plantains, sometimes referred to as cooking bananas, excel in savory dishes. They are integral to recipes such as tostones, mofongo, and pastelón, a traditional dish from Puerto Rico.
Nutritional Benefits and Dietary Roles
Both bananas and plantains are rich sources of vital nutrients, including potassium, vitamin C, and dietary fiber, which contribute to digestive health and overall well-being. Bananas typically contain higher sugar levels and fewer complex carbohydrates, providing a quick source of energy. Plantains, with their greater complex carbohydrate content, offer sustained energy and may even assist in lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease.
The differences in their roles within a diet are notable. While bananas are ideal for raw snacking, plantains are culinary staples in various African and Latin American cuisines. The primary distinction lies in their flavor profiles and how they are used in cooking. For those seeking a sweet and portable snack, bananas are the clear choice. However, if one is looking for a starchy side or exploring savory cooking, plantains are the preferred option.
Understanding these differences can enhance culinary experiences. When selecting fruits at the market, consider the size, shape, and skin texture. Green bananas can ripen at home, but unripe plantains are best cooked before consumption.
This exploration of bananas and plantains highlights not only their unique characteristics but also their significance in diverse cuisines around the world. Whether enjoyed in a sweet dish or a savory meal, both fruits offer valuable nutrients and flavors that appeal to a wide range of tastes.
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoDiscover the Best Wireless Earbuds for Every Lifestyle