Health
First Documented Death from Alpha-Gal Syndrome Sparks Alarm
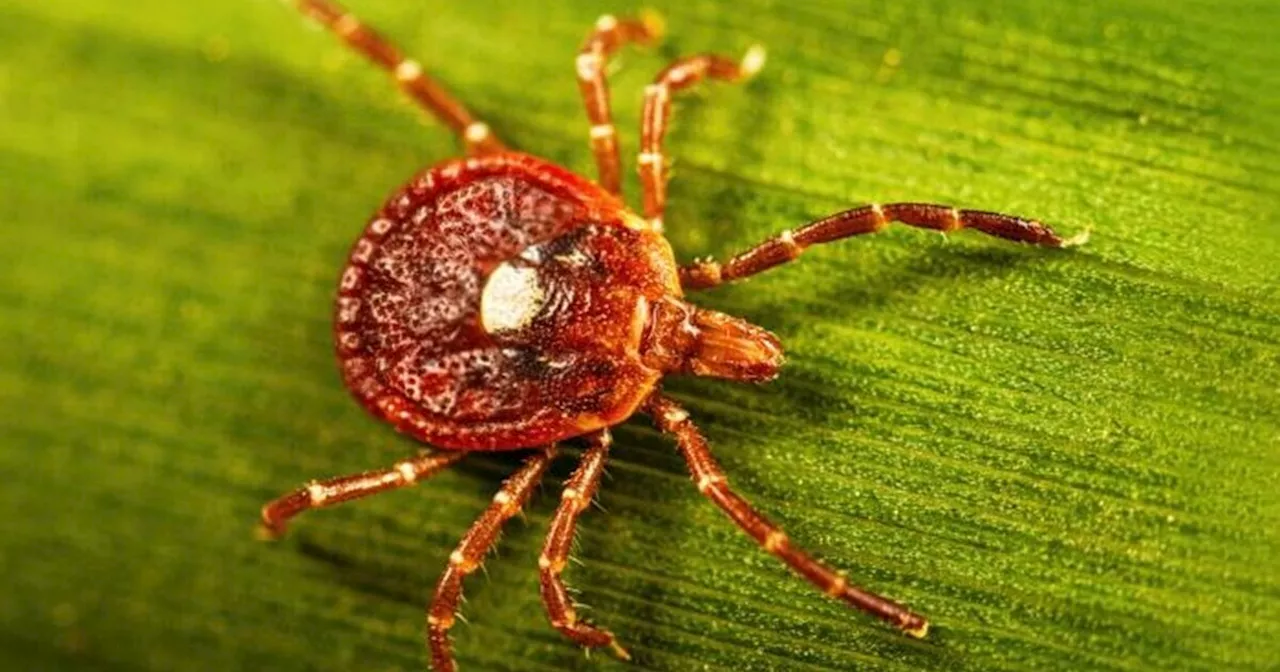

Researchers have documented the first known death attributed to alpha-gal syndrome, a serious allergic reaction to red meat linked to bites from the lone star tick. The case involves a 47-year-old pilot from New Jersey who died after consuming a hamburger at a barbecue in 2024. This alarming incident underscores the critical need for heightened awareness surrounding tick-borne allergies and their potential consequences.
The findings, published by the University of Virginia School of Medicine, detail how the pilot fell ill approximately four hours after eating. His son discovered him unconscious in a bathroom, surrounded by vomit. Despite immediate medical intervention, he was pronounced dead at a nearby hospital. The autopsy indicated a cause of death as a sudden unexplained event, emphasizing the severity and unpredictability of alpha-gal syndrome.
This tragic case reveals crucial insights into the progression of the disease, particularly for individuals who remain undiagnosed. The pilot’s wife noted that he had previously experienced symptoms such as abdominal discomfort and nausea after consuming red meat, which were initially mistaken for food poisoning. These symptoms highlight the challenges in recognizing and diagnosing alpha-gal syndrome effectively.
Prior to the fatal incident, the pilot had similar reactions after eating a steak dinner. Despite the alarming patterns, he and his wife did not seek medical help. A blood sample taken post-mortem confirmed an allergic reaction, while further investigation identified multiple bites from lone star ticks, known carriers of alpha-gal syndrome. These bites, initially misidentified as chigger bites, likely triggered the development of the allergy.
Alpha-gal syndrome is characterized by an allergic response to alpha-gal, a sugar molecule found in mammals. When the pilot consumed red meat, his body mounted a severe immune response, resulting in a fatal allergic reaction. Experts stress the increasing prevalence of lone star ticks in various regions, which contributes to the rising number of reported cases of alpha-gal syndrome.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has indicated a significant uptick in confirmed cases, estimating that as many as 450,000 people in the United States could be affected. This discrepancy between confirmed and actual cases is attributed to delayed diagnoses and a lack of awareness among both healthcare providers and patients.
The pilot’s experience serves as a stark reminder of the potential dangers of this allergy and the importance of early detection and management. The American Gastroenterological Association recommends testing for alpha-gal syndrome in patients presenting unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain.
The growing prevalence of lone star ticks, particularly in the United States, poses an escalating public health challenge. Experts attribute this rise to climate changes that allow these ticks to migrate into new habitats, thus expanding the geographic reach of alpha-gal syndrome. Consequently, more individuals are exposed to the risk of developing the allergy.
Preventative measures are essential in combating this health concern. Recommendations include using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding areas where ticks thrive. In the event of a tick bite, it is crucial to remove the tick promptly. Retaining the tick in a sealed bag can assist healthcare providers in identifying the species and testing it for diseases, allowing for quicker responses to potential infections.
Currently, no vaccine exists for alpha-gal syndrome, and the primary management strategy involves dietary changes, specifically the elimination of red meat. The pilot’s unfortunate death underscores the urgent need for public education regarding alpha-gal syndrome, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and comprehensive training for healthcare professionals about its symptoms and management strategies.
As awareness grows, so too does the need for research into effective prevention and treatment methods. The increase in both the number of cases and the expansion of tick populations highlights the importance of addressing this significant public health issue.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoHarmonic Launches AI Chatbot App to Transform Mathematical Reasoning