Education
Illinois Enacts Key Education Laws Focused on AI and Immigrant Rights
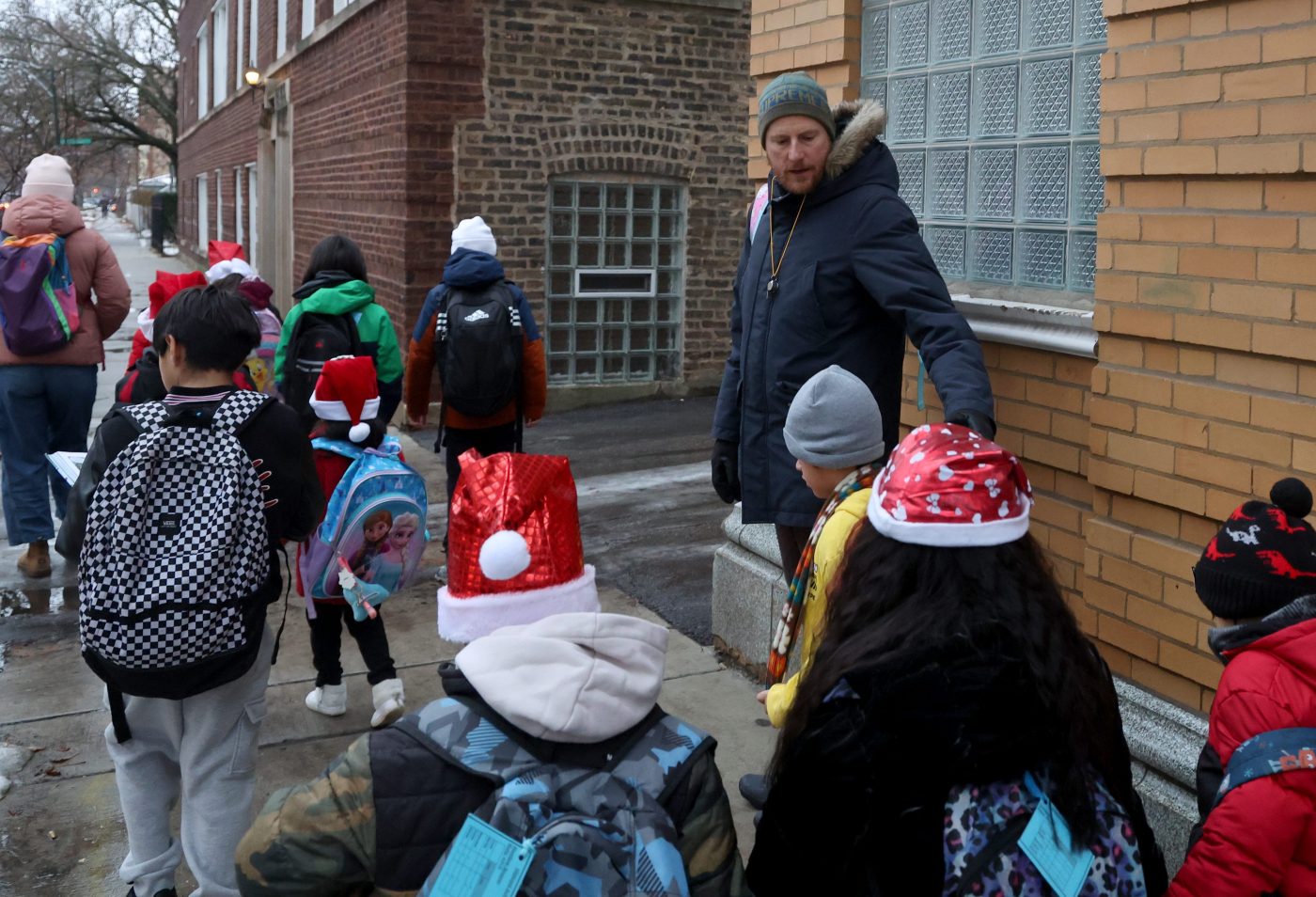

New education laws in Illinois, effective in 2026, aim to enhance the rights of immigrant students and regulate the growing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in schools. These changes highlight the state’s commitment to ensuring equitable access to education while addressing emerging technologies in the classroom.
Strengthening Rights for Immigrant Students
One significant amendment to the Illinois School Code prohibits public schools from denying students access to free education based on their immigration status or that of their parents. This measure reinforces long-standing federal protections amid increasing scrutiny of immigrant rights, particularly during periods of heightened federal immigration enforcement.
Proponents of this legislation emphasize its importance in safeguarding educational opportunities for all students. Lawrence Benito, executive director of the Illinois Coalition for Immigrant and Refugee Rights, stated, “In the face of federal threats to our schools and students, our communities came together and organized to demand that our state leaders stand up for education for all Illinois children.”
Moreover, schools are now prohibited from excluding noncitizen children from participating in programs or activities, ensuring inclusivity within the educational system.
Regulating AI in Education
As artificial intelligence continues to influence learning environments, new laws require the Illinois State Board of Education to provide guidance on its ethical and responsible use in K-12 settings. This guidance will cover fundamental concepts of AI, its functionality, and its potential applications in classrooms.
Additionally, schools must be informed about the implications of AI on student data privacy. The new regulations also stipulate that community college courses cannot be taught solely by AI or generative AI programs, ensuring that human instructors remain central to the educational experience.
Supporters of these regulations argue that they will mitigate potential threats to public safety and personal privacy while fostering innovation in educational practices. This approach contrasts with the previous administration’s stance, which promoted the unregulated adoption of AI across various sectors.
Enhancements in Special Education Resources
Illinois schools are now mandated to provide written notifications to parents or guardians of students with disabilities regarding their rights to have an advocate present at meetings about their child’s individualized education program (IEP). This legal document is crucial for accessing special education services.
House Bill 2994 further enhances parental access to information about their children’s mental health records, fostering transparency and support for families navigating special education processes.
New Opportunities for Student Advancement
In a push to expand educational opportunities, seventh and eighth-grade students can now earn high school credits by successfully completing courses at their future high schools. Additionally, high school students will have access to a comprehensive catalog of internships, externships, and volunteer opportunities, which will be made available annually on the State Board of Education’s website.
Students may also participate in work-based learning experiences that count toward their school day, provided they receive approval from licensed educators. Programs designed for gifted and talented students will also enjoy increased flexibility in their structure.
Updated Policies for Higher Education Institutions
New requirements for public and private universities include posting the cost of attendance on their websites. Public universities and colleges must ensure the availability of at least three on-site mental health professionals to support student well-being.
These changes aim to enhance transparency and accessibility within Illinois’ higher education system, contributing to a more informed student body.
Broader Changes to Statewide Education
Additional modifications to the educational landscape in Illinois encompass early literacy initiatives and data transparency measures. All school districts are now required to screen and report early literacy scores for K-3 students to the State Board of Education.
The state board will also gather data on funding aimed at supporting homeless students, making this information publicly accessible. Additionally, Illinois school districts must develop educational materials promoting the benefits of American Sign Language, which will be shared with K-8 schools and posted on the State Board of Education’s website by July 1.
These reforms represent a significant shift in Illinois’ education policies, reflecting a commitment to inclusivity, innovation, and the well-being of all students. The initiatives are expected to foster a more equitable and supportive educational environment across the state.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide