Science
Scientists Propose Strategies to Prevent Asteroid Impact on Moon
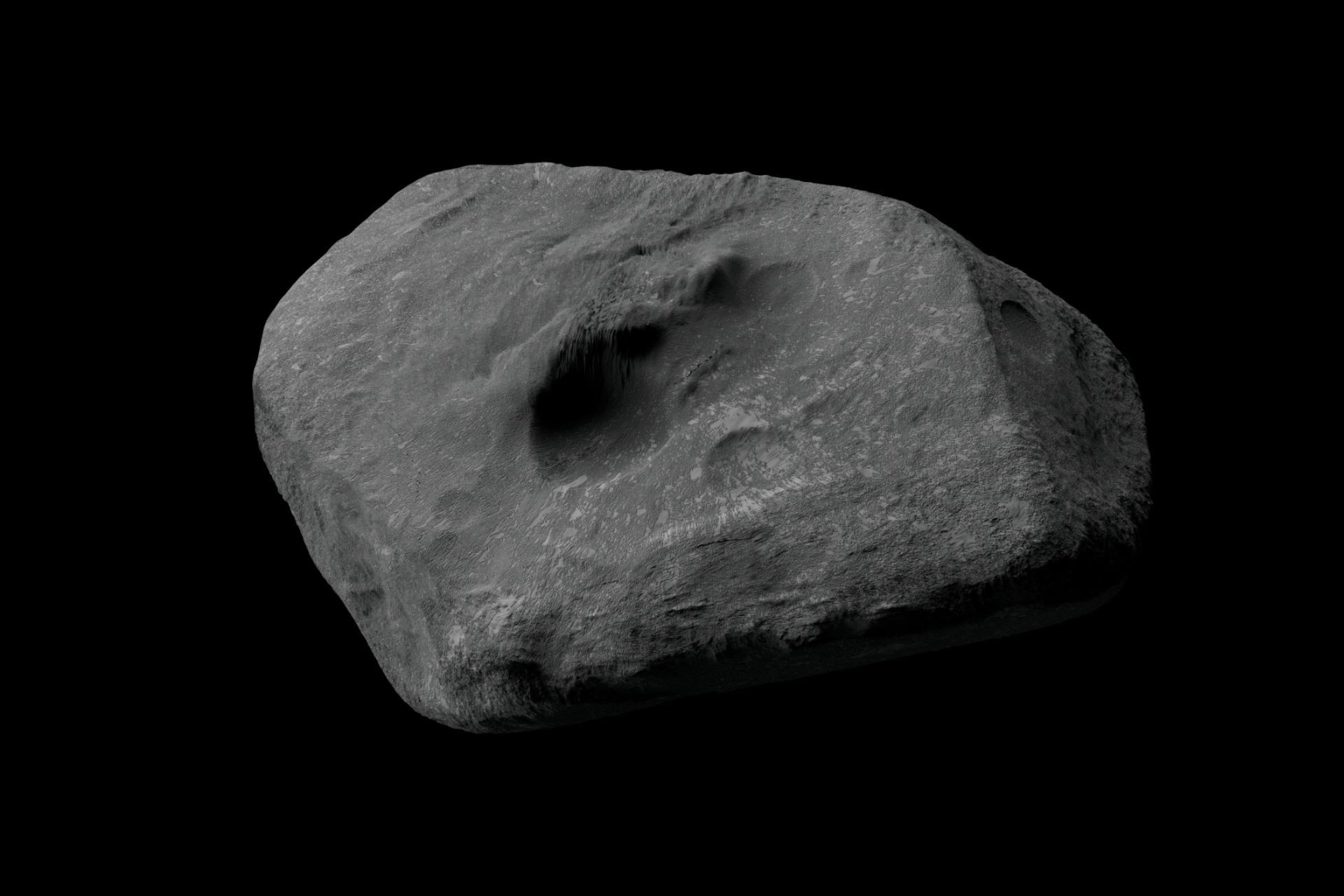

In a significant development, astronomers have identified a potential threat from asteroid 2024 YR4, which could collide with the Moon in 2032. Although the likelihood of this impact is relatively low, at approximately 4%, researchers from NASA and other U.S. institutions emphasize the need for preparedness. The asteroid previously raised alarms regarding a possible collision with Earth, a scenario that has since been ruled out, but its trajectory still poses a risk to lunar safety.
Recent studies suggest that if 2024 YR4 were to strike the Moon, it could eject a vast amount of micrometeoroid debris into low-Earth orbit. This debris could jeopardize the safety of spacecraft and astronauts aboard the International Space Station. A paper outlining various strategies for dealing with this potential threat has been submitted to the Journal of the Astronautical Sciences and is currently under peer review.
Exploring Options for Asteroid Mitigation
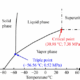
The authors of the study evaluate multiple methods to either deflect or destroy the asteroid before it could impact the Moon. Traditionally, deflecting an asteroid is the preferred method for preventing a collision. However, doing so with 2024 YR4 presents significant challenges. Deflection would ideally eliminate the threat of impact; yet, if executed poorly, it could create numerous smaller fragments that may pose unpredictable risks.
NASA successfully demonstrated asteroid deflection techniques in 2022 with its DART mission (Double Asteroid Redirection Test), which altered the trajectory of the asteroid moonlet Dimorphos. Despite this success, the complexity of deflecting 2024 YR4 cannot be understated. To calculate the necessary energy for deflection, astronomers require precise data regarding the asteroid’s mass and density.
The James Webb Space Telescope recently measured 2024 YR4’s diameter at approximately 60 meters (197 feet). However, the asteroid’s mass remains uncertain, with estimates ranging from 33 million kilograms (74 million pounds) to more than 930 million kilograms (2 billion pounds). This uncertainty complicates the calculations required for effective deflection, as miscalculating the required energy could inadvertently redirect the asteroid toward Earth.
The researchers suggest that NASA could undertake a reconnaissance mission to gather more accurate data about 2024 YR4, but the optimum launch window for such a mission would be in 2028. This leaves a tight timeline of only three years to finalize the mission, raising concerns about the feasibility of this approach.
The Case for Destruction
Given the uncertainties associated with deflection, the researchers advocate for a more aggressive strategy: destroying the asteroid. They present a couple of viable options for NASA to consider. The first is a robust kinetic disruption mission, akin to the DART mission, but aimed at breaking the asteroid apart rather than nudging it off course. This method, while not previously tested, could be developed within a reasonable timeframe, with the next launch window available between April 2030 and April 2032.
An alternative strategy involves the use of a nuclear device to destroy 2024 YR4. This would entail detonating a nuclear device on or near the asteroid’s surface to fragment it. Although this approach has not been tested, it remains a theoretically viable option. The researchers indicate that the next possible launch window for such a mission would be from late 2029 to late 2031.
As the potential close approach of asteroid 2024 YR4 draws nearer, scientists recognize the importance of utilizing this opportunity to advance our understanding of planetary defense. While the asteroid is expected to pass safely by the Moon, its presence serves as a critical reminder of the need for preparedness against celestial threats. By refining strategies to mitigate impacts, scientists can better safeguard Earth and its natural satellite in the future.
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoDiscover the Best Wireless Earbuds for Every Lifestyle