Science
Researchers Uncover Cholesterol Pathway Breakthrough in Gastric Cancer
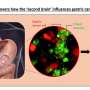
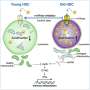
A research team from the LKS Faculty of Medicine at the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed) has achieved a significant milestone in understanding gastric cancer. Their study reveals how the enteric neurons, often referred to as the “second brain,” can influence both tumor growth and the effectiveness of treatments. This discovery highlights the role of cholesterol pathways in cancer progression, suggesting new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
The researchers found that by blocking specific cholesterol pathways, tumor growth in mice was reduced by an impressive 65%. This groundbreaking finding provides a new perspective on the metabolic mechanisms that drive gastric cancer, which remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally.
Understanding the Role of Enteric Neurons
Enteric neurons are part of the nervous system located in the digestive tract, playing a crucial role in regulating gastrointestinal functions. The study indicates that these neurons can significantly impact how tumors develop and respond to treatment. By investigating the interactions between these neurons and cancer cells, the research team uncovered critical insights into the tumor microenvironment.
Dr. Christine Choi, the lead researcher at HKUMed, emphasized the importance of this discovery. “Our findings suggest that enteric neurons are not merely passive observers in the cancer landscape; they actively participate in shaping tumor behavior,” she stated. The research highlights the need to consider the nervous system’s influence in developing strategies for treating gastric cancer effectively.
Implications for Future Cancer Treatments
The implications of this research extend beyond gastric cancer. By understanding the metabolic pathways influenced by enteric neurons, scientists may develop targeted therapies that disrupt these pathways, potentially leading to more effective cancer treatments. The study opens the door to exploring how dietary and lifestyle changes could impact cancer progression by affecting cholesterol metabolism.
Further investigations are planned to assess how these findings can be translated into clinical practice. The research team aims to collaborate with oncologists to explore the feasibility of targeting cholesterol pathways in human patients suffering from gastric cancer.
This study, published in a peer-reviewed journal, underscores the importance of multidisciplinary approaches in cancer research. It combines insights from molecular biology, neuroscience, and oncology, paving the way for innovative treatment strategies that could improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
As the fight against cancer continues, breakthroughs like this one offer hope and highlight the intricate connections between various biological systems. The research team’s findings represent a step forward in unraveling the complexities of gastric cancer and illustrate the potential for future advancements in cancer therapy.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods