Science
New Technique Speeds Drug Design Targeting Ion Channels
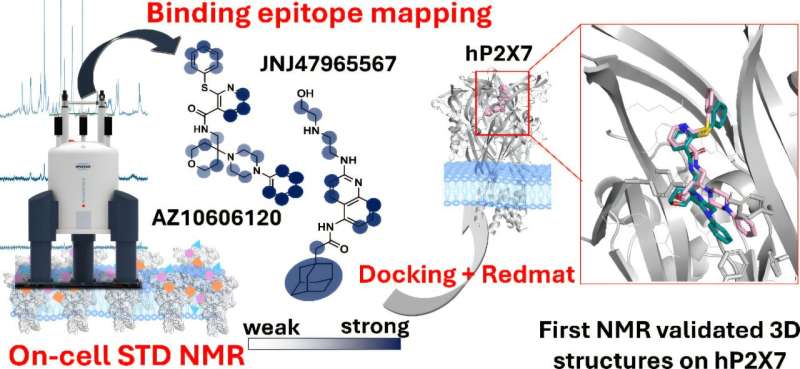
An international research team has unveiled a groundbreaking technique that significantly accelerates the design of drugs targeting ion channels, proteins closely linked to a variety of diseases, including psychiatric disorders and different forms of cancer. This innovative approach, developed by the Institute of Chemical Research, a collaboration between the University of Seville and the Spanish National Research Council, was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on November 15, 2025.
Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that control the flow of ions into and out of cells, playing crucial roles in various physiological processes such as nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and immune responses. Dysfunction in these channels is associated with numerous medical conditions, making them prime targets for therapeutic intervention.
Revolutionizing Drug Interaction Studies
Traditionally, the study of how drugs interact with ion channels required isolating these proteins, a complex process that could alter their natural behavior. According to Jesús Angulo from the Institute of Chemical Research, the new technique employs nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to study these interactions in living cells, yielding more relevant biological insights.
“This technique is faster, more cost-effective, and simpler, as it removes the need for extensive protein purification and manipulation,” Angulo stated. The researchers believe this method could establish a new standard in structure-activity relationship studies, which explore how a molecule’s chemical structure influences its pharmacological effects.
Broader Implications for Multiple Diseases
The technique has been successfully tested on P2X7 receptors, which are therapeutic targets for conditions such as depression, certain autism spectrum disorders, and some cancers. Leanne Stokes of the University of East Anglia emphasized the potential of this method: “Our technique could significantly accelerate the development of drugs targeting ion channels and other membrane proteins, opening new avenues for research in neurological, cardiovascular, metabolic, and oncological diseases.”
Furthermore, the researchers utilized software developed at IIQ-CSIC-US to integrate their experimental findings with three-dimensional models of drug-receptor interactions, generated through bioinformatics. This advancement allowed them to validate which computational models aligned with their laboratory observations.
“The interaction between drug and protein can be likened to a lock and key: the membrane protein is the lock, and our drug is the key,” Angulo explained. “Identifying the correct key and determining how to insert it for optimal function is crucial.” He further noted that bioinformatic models play a vital role in drug design and that validating three-dimensional computer-generated models in living cells signifies a transformative approach in developing drugs aimed at these proteins.
This research not only enhances the understanding of drug interactions but also holds promise for more effective and targeted treatments for a range of diseases, marking a significant step forward in pharmacological studies.
For further details, refer to the study: Serena Monaco et al, “On-Cell Saturation Transfer Difference NMR Spectroscopy on Ion Channels: Characterizing Negative Allosteric Modulator Binding Interactions of P2X7,” published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoHarmonic Launches AI Chatbot App to Transform Mathematical Reasoning
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup















