Science
Microgravity Manufacturing: Varda Space Industries Pioneers Drug Development

In a significant advancement for the pharmaceutical industry, Varda Space Industries is leveraging microgravity to develop new drug formulations that are not possible on Earth. During a recent episode of the podcast Space Minds, host David Ariosto spoke with Will Bruey, CEO and co-founder of Varda, who discussed how the company is transforming drug manufacturing in space. By utilizing microgravity, Varda aims to enhance the formulation process and bring innovative pharmaceutical solutions back to Earth.
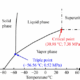
Varda’s approach hinges on the unique environment of microgravity, which allows for new chemical outcomes. Bruey explained that the absence of gravity can modify the way drugs are formulated, akin to adjusting temperature in traditional manufacturing. “We want to introduce a gravity knob to the pharmaceutical industry,” Bruey stated. This method opens avenues for creating formulations that might improve patient experiences, such as transforming intravenous (IV) medications into more accessible forms like subcutaneous shots.
The economic landscape for space launches has evolved dramatically in recent years, making Varda’s business model viable. Previously, high launch costs and unpredictable schedules hindered the potential for in-space manufacturing. However, advancements such as the Falcon 9 rocket have established a reliable launch cadence, which Bruey noted has fundamentally changed the industry. “Space is now just shipping,” he remarked, emphasizing the shift from national efforts to commercial opportunities.
Addressing Challenges and Scaling Operations
Varda is currently refining its processes and scaling operations, running its microgravity manufacturing system, dubbed the “microgravity oven,” four times a year. Bruey indicated that while this frequency is currently limited, the goal is to increase both the number of launches and reduce costs, thereby improving the economic feasibility of producing pharmaceuticals in space.
The company plans to focus on manufacturing active pharmaceutical ingredients in its re-entry vehicles rather than full drug formulations, which would minimize costs and streamline operations. “We’re only shipping the active ingredients to space and back,” Bruey explained. This approach positions Varda to capitalize on a sizable market for pharmaceuticals, which are among the most valuable chemicals produced on Earth.
Despite the promising outlook, Bruey acknowledged potential hurdles, including regulatory challenges and supply chain logistics. For example, the FDA will require comprehensive plans for redundancies in supply chains, especially for life-saving drugs manufactured in space. Nevertheless, Bruey expressed confidence that the launch market would adapt to meet the demand created by Varda’s innovative manufacturing processes.
Looking Ahead: Hypersonic Applications and Future Developments
As Varda continues to establish itself in the pharmaceutical sector, the company is also exploring hypersonic applications for its re-entry vehicles. Bruey suggested that the same technology used for transporting pharmaceuticals could be adapted for hypersonic travel, which remains a frontier in aerospace innovation. He described Varda’s re-entry vehicle as “the cheapest way to go from space to Earth,” noting that its design also makes it suitable for hypersonic speeds.
With a projected timeline of approximately ten years for drug development from molecule to market, Varda is positioning itself to become a key player in the future of pharmaceuticals. Bruey indicated that the company aims to have formulations ready for clinical trials by the end of this decade, focusing initially on reformulations of existing drugs to expedite the approval process.
The combination of microgravity manufacturing and advancements in space technology has the potential to reshape the pharmaceutical landscape. As Varda Space Industries continues to innovate, the implications for healthcare and drug accessibility may be profound, possibly leading to breakthroughs that were once considered unattainable. The journey into space may very well lead to the next generation of medical solutions for patients on Earth.
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoDiscover the Best Wireless Earbuds for Every Lifestyle