Science
Astronomers Discover Early Barred Spiral Galaxy, COSMOS-74706
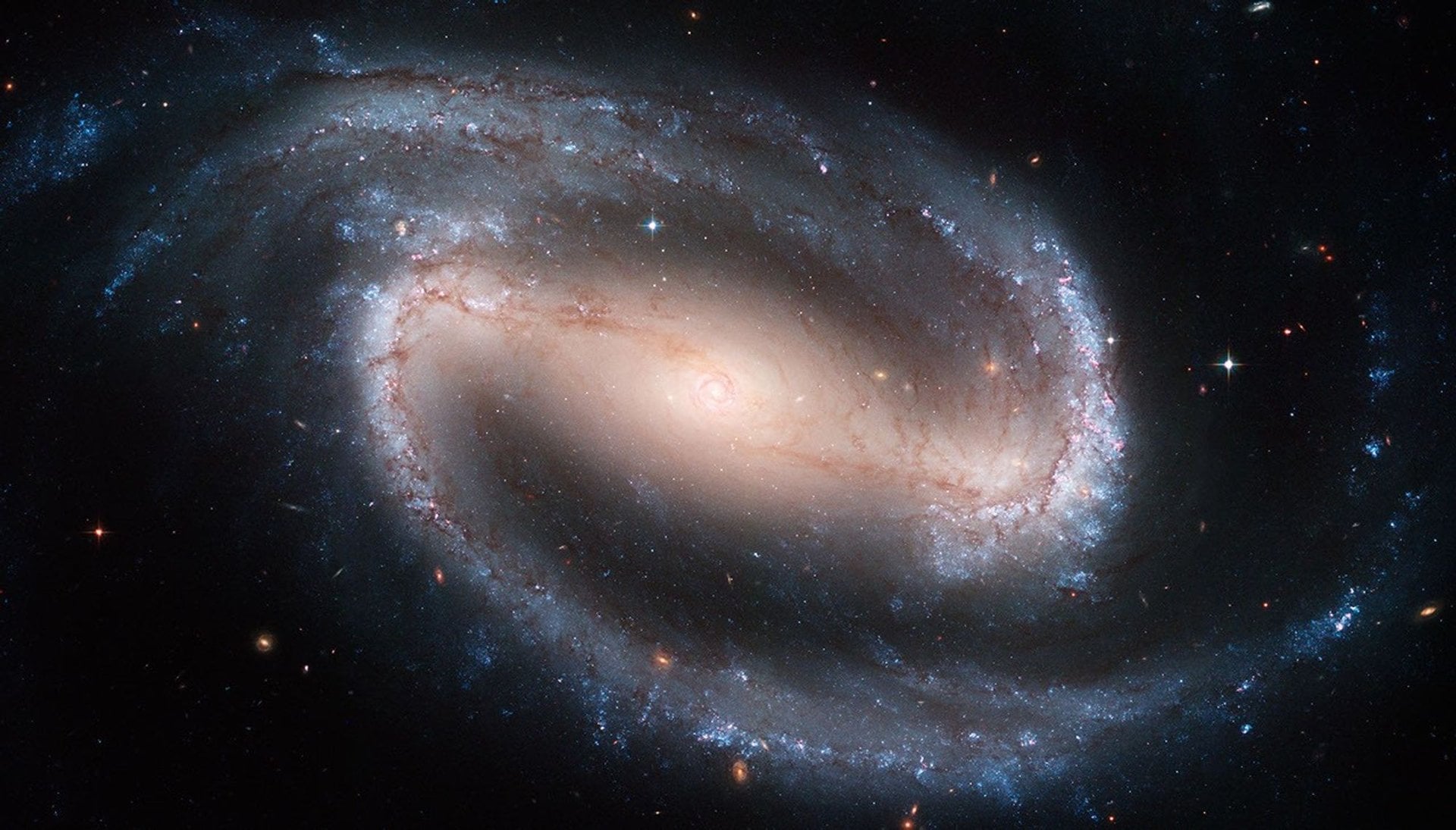

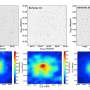
Astronomers have identified what could be the earliest barred spiral galaxy, named COSMOS-74706, existing approximately 11.5 billion years ago. This groundbreaking discovery, made possible by advanced instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), offers new insights into the timeline of galaxy formation and evolution following the Big Bang.
The research, led by Daniel Ivanov, a graduate student in physics and astronomy at the University of Pittsburgh, was presented on January 8, 2026, during the 247th meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) in Phoenix, Arizona. The team utilized data from the JWST’s spectrometers, which allowed for a more precise determination of the galaxy’s age compared to previous methods that relied on gravitational lensing or redshift measurements.
Understanding Barred Spiral Galaxies
Barred spiral galaxies, including our own Milky Way, feature a distinctive bar-shaped structure of stars across their centers. This configuration plays a crucial role in the galaxy’s evolution by directing gas inward from the outer regions, thereby feeding the supermassive black hole at the center and regulating star formation throughout the stellar disk.
According to the Hubble Sequence, galaxies typically begin as spheroidal masses with minimal gas and dust before evolving into spiral forms characterized by their arms radiating from a central bulge. The discovery of COSMOS-74706 sheds light on the formation of barred structures in galaxies, suggesting that bars may have begun to appear as early as 12.5 billion years ago, although observational evidence has been sparse.
Significance of the Discovery
While other barred spiral galaxies have been identified as potentially older, those findings have often been inconclusive due to the limitations of the observational methods employed. Gravitational lensing can distort light and obscure accurate measurements, while redshift calculations carry a margin of error of 10-15%. The use of spectroscopy in the case of COSMOS-74706 provides a clearer and more reliable validation of its age.
Ivanov emphasized the importance of this discovery in a press release from the University of Pittsburgh. He noted that the presence of such an early barred spiral galaxy contributes significantly to our understanding of galactic evolution and the timeline of structure formation in the universe.
The identification of COSMOS-74706 not only enriches our knowledge of the early universe but also serves as a platform for future research into the complexities of galaxy formation. As astronomers continue to utilize advanced technology, the potential for uncovering more secrets of the cosmos remains vast and exciting.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide