Health
New Research Reveals Immune Mechanisms Behind Multiple Sclerosis

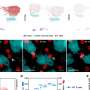
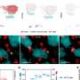
New research provides significant insights into the immune signals that contribute to inflammation in multiple sclerosis (MS). This chronic neurological disease affects approximately 2.8 million individuals globally, leading to damage to the nerve fibers in the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. The immune system in these patients mistakenly attacks myelin, the protective sheath surrounding the axons, resulting in various neurological impairments, including issues with vision, movement, and cognitive function.
Researchers have identified specific immune signals that drive this inflammatory process, offering a clearer understanding of how MS develops. The findings, published in a leading neurology journal, could pave the way for new therapeutic strategies aimed at modulating the immune response in MS patients.
The study highlights how inflammation is not just a side effect but a key player in the progression of the disease. Understanding the role of these immune signals may lead to targeted treatments that could slow down or even halt the progression of MS, potentially improving the quality of life for many affected individuals.
Importance of Understanding Immune Mechanisms
The immune response in MS is complex, involving various signaling pathways that contribute to the inflammatory environment in the central nervous system. By identifying these pathways, the research team aims to establish a clearer link between immune activity and disease progression. This could ultimately lead to more effective treatments tailored to the underlying mechanisms of the disease rather than merely addressing symptoms.
The researchers involved in the study underscore the critical need for further exploration into these immune signals. They emphasize that understanding how the immune system interacts with nervous tissue can shed light on not only MS but also other neurological disorders characterized by similar inflammatory processes.
Potential Impact on Treatment Strategies
This research could have far-reaching implications for the treatment of MS. Current therapies often focus on suppressing the immune system, which can leave patients vulnerable to infections and other complications. By targeting specific immune signals involved in the inflammatory process, new therapies could enhance the effectiveness of treatment while minimizing adverse effects.
As the understanding of the immune mechanisms driving MS continues to evolve, there is hope for developing personalized medicine approaches that are more effective and have fewer side effects. The authors of the study advocate for increased funding and research efforts to translate these findings into clinical practice.
In conclusion, the new insights into the immune signals that drive inflammation in multiple sclerosis mark a significant step forward in understanding this debilitating disease. With ongoing research, there is potential for breakthroughs that could transform the lives of millions living with MS, making it imperative to continue advancing this vital area of medical science.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide