Technology
New DNA Model Predicts Variant Effects, Enhances Disease Diagnosis

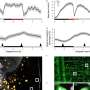
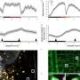
A novel framework named GPN-MSA has been developed to predict the effects of genome-wide variants more accurately, significantly advancing the understanding of both coding and noncoding regions of the human genome. Traditionally, protein language models have excelled at predicting the impacts of missense variants. However, DNA language models have struggled to demonstrate similar efficacy, particularly when addressing the complexities inherent in the human genome, which is composed of approximately 98% noncoding regions.
The GPN-MSA framework leverages whole-genome alignments across multiple species, making it a unique tool in genomic research. Remarkably, the model can be trained in just a few hours, providing a timely option for researchers. Rigorous testing across various clinical databases, functional assays, and population genomic data has shown that GPN-MSA excels in predicting the deleteriousness of variants, marking a significant milestone in genetic research.
One of the standout features of this model is its ability to generate precomputed scores for all approximately 9 billion possible single-nucleotide variants in the human genome. This comprehensive data set is expected to play a crucial role in enhancing the accuracy of rare disease diagnoses and facilitating rare variant burden testing. The research team anticipates that these advancements will lead to better clinical outcomes for patients with complex genetic conditions.
The findings are detailed in a study co-authored by prominent researchers including Goldfeder, R. L., Wall, D. P., Khoury, M. J., Ioannidis, J. P., and Ashley, E. A.. Their research is supported by substantial backing from the National Institutes of Health and the Koret–UC Berkeley–Tel Aviv University Initiative in Computational Biology and Bioinformatics.
The GPN-MSA framework not only represents a significant technical achievement but also sets the stage for future discoveries in genetic diagnostics. With its high-performance predictions, GPN-MSA is poised to become a vital resource for researchers and clinicians alike. The pretrained model and its associated datasets are accessible through various platforms, ensuring that the scientific community can utilize these advancements effectively.
In conclusion, the introduction of GPN-MSA marks a pivotal moment in genomic research, providing a new avenue for understanding the complex interactions of genetic variants within the human genome. The implications for rare disease diagnosis and treatment could be profound, heralding a new era of personalized medicine that leverages the power of advanced computational tools.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide