Science
Tiny Robots Navigate Bloodstream for Targeted Drug Delivery

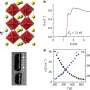
Scientists at ETH Zurich in Switzerland have developed a groundbreaking robot, measuring just the size of a grain of sand, that can navigate the bloodstream to deliver drugs with remarkable precision. This innovation promises to enhance treatment efficacy while significantly reducing the side effects commonly associated with traditional drug delivery methods.
The tiny robots are controlled by external magnetic fields, allowing for targeted delivery to specific sites within the human body. This method not only increases the effectiveness of medications but also minimizes the risk of damage to healthy tissues. According to the research team, this advancement could transform the way that chronic diseases are treated, paving the way for more personalized medical interventions.
Technology Behind the Breakthrough
The tiny robots function through a combination of magnetic control and sophisticated engineering. Each robot is designed to respond to magnetic fields, which guide their movement through the complex network of the human circulatory system. This precise navigation system allows for targeted drug delivery, ensuring that medications reach the intended location without affecting surrounding tissues.
In laboratory tests, the robots demonstrated the ability to travel through simulated blood vessels, showcasing their potential for real-world medical applications. The researchers believe that this technology could be particularly beneficial for delivering treatments for conditions such as cancer, where targeted therapy is crucial to minimize collateral damage to healthy cells.
The research team has highlighted that the robots can be engineered to carry various types of drugs, from chemotherapy agents to anti-inflammatory medications. This versatility opens up a wide range of possibilities for future medical treatments.
Potential Impact on Healthcare
The implications of this technology extend beyond mere convenience in drug delivery. By ensuring that medications are administered precisely where needed, the tiny robots could help to improve patient outcomes and streamline the overall healthcare process. Reducing the side effects associated with systemic drug administration may encourage more patients to pursue necessary treatments, ultimately enhancing quality of life.
The study, published in a leading medical journal in 2023, underscores the importance of innovation in the medical field. As healthcare systems worldwide grapple with the challenges of chronic illnesses and aging populations, this technology offers a glimpse into the future of personalized medicine.
The research at ETH Zurich is part of a broader trend towards integrating advanced technologies into healthcare, where robotics and artificial intelligence are increasingly playing vital roles. As this field develops, collaboration among scientists, engineers, and medical professionals will be essential to bring these innovations from the lab to clinical practice.
In summary, the creation of these tiny robots represents a significant leap forward in drug delivery systems, potentially changing the landscape of medical treatments. As research continues, the hope is to see these advancements translated into real-world applications that enhance patient care and outcomes globally.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods