Science
Surprising Mechanisms of Flower Pollination Revealed
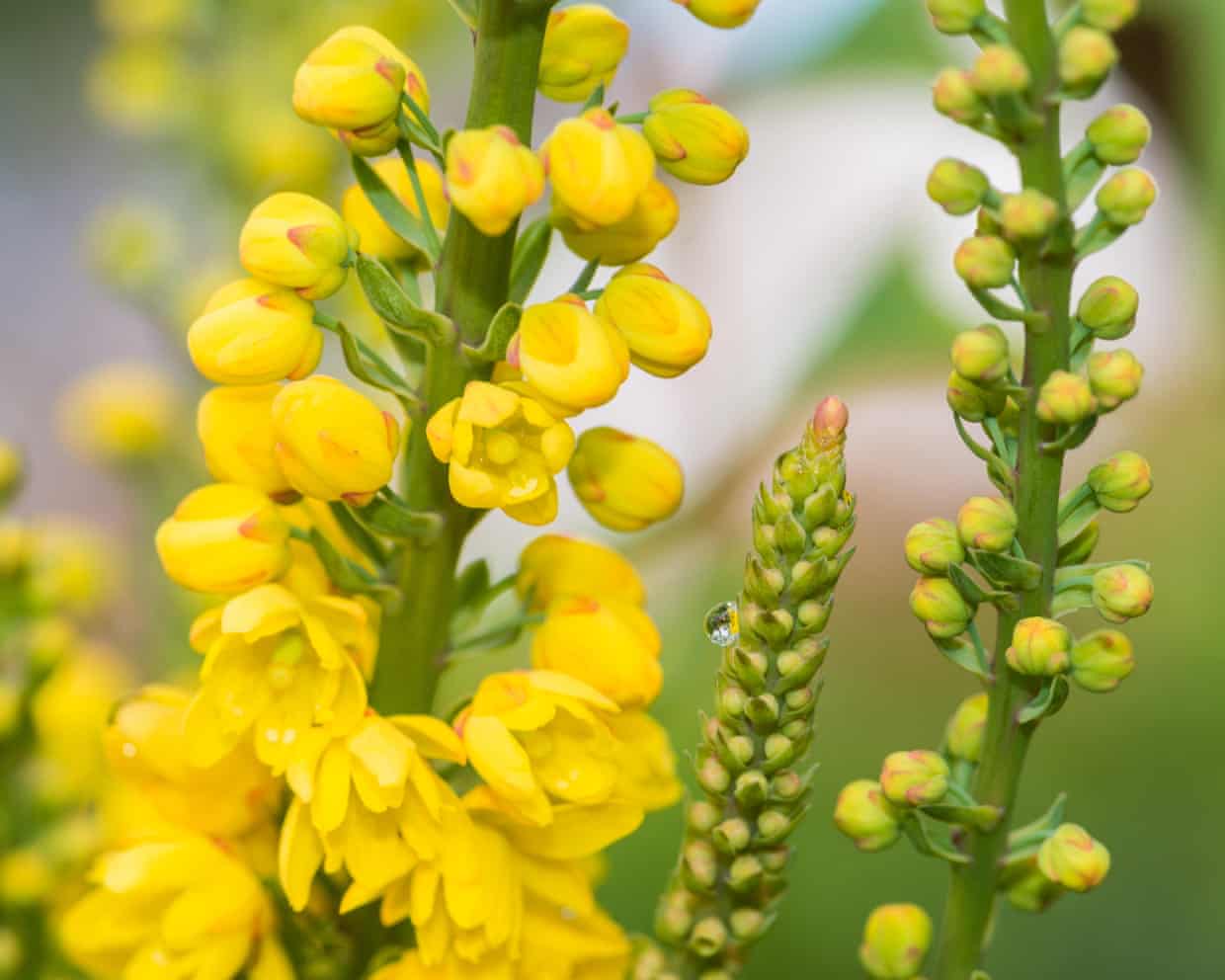

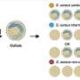
Recent research has unveiled fascinating behaviors among flower species, specifically regarding their male reproductive parts, the stamens. These mechanisms play a crucial role in attracting pollinators while ensuring efficiency in nectar and pollen utilization. In plants such as Berberis and Mahonia, touch-sensitive stamens engage in rapid movements that can be triggered repeatedly, creating a unique interaction with visiting insects.
When insects approach these flowers to access nectar, they often encounter stamens that swiftly bend over, depositing pollen directly onto the insect’s face or tongue. This unexpected contact prompts the insect to make a quick exit, minimizing the time spent at the flower. As a result, the flower conserves its nectar and pollen, increasing its chances of successful pollination when the insect visits another flower, where it can transfer the pollen to receptive female organs.
Dynamic Responses of Other Flower Species
The orchid species Catasetum showcases an even more aggressive approach to pollination. Insects that land on these flowers are met with a rapid release of sticky pollen bags, which are ejected with such force that they may knock the insect out of the flower. This mechanism ensures that the pollen adheres to the insect’s body, facilitating the transfer of genetic material when it visits another flower.
In Australia, the triggerplants of the genus Stylidium employ a remarkable strategy. These plants possess a club-shaped organ that swings through 180 degrees in just 10 milliseconds when touched. This swift movement delivers a pollen strike to the visiting insect while simultaneously collecting any pollen it may be carrying. After this interaction, the trigger resets quickly, allowing it to engage with the next pollinator.
The intricate designs and strategies employed by these plants highlight the complex relationship between flowers and their pollinators. By developing mechanisms that enhance cross-pollination while conserving resources, these species have evolved to optimize their reproductive success.
Understanding these interactions is vital for conservation efforts and agricultural practices, as pollinators are essential for the health of ecosystems and food production. Continued research into the diverse strategies of various plant species will shed light on how to protect these vital relationships and ensure the sustainability of pollination processes worldwide.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoHarmonic Launches AI Chatbot App to Transform Mathematical Reasoning
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride