Science
Scientists Launch World’s First Cellular Atlas of Aedes aegypti Mosquito
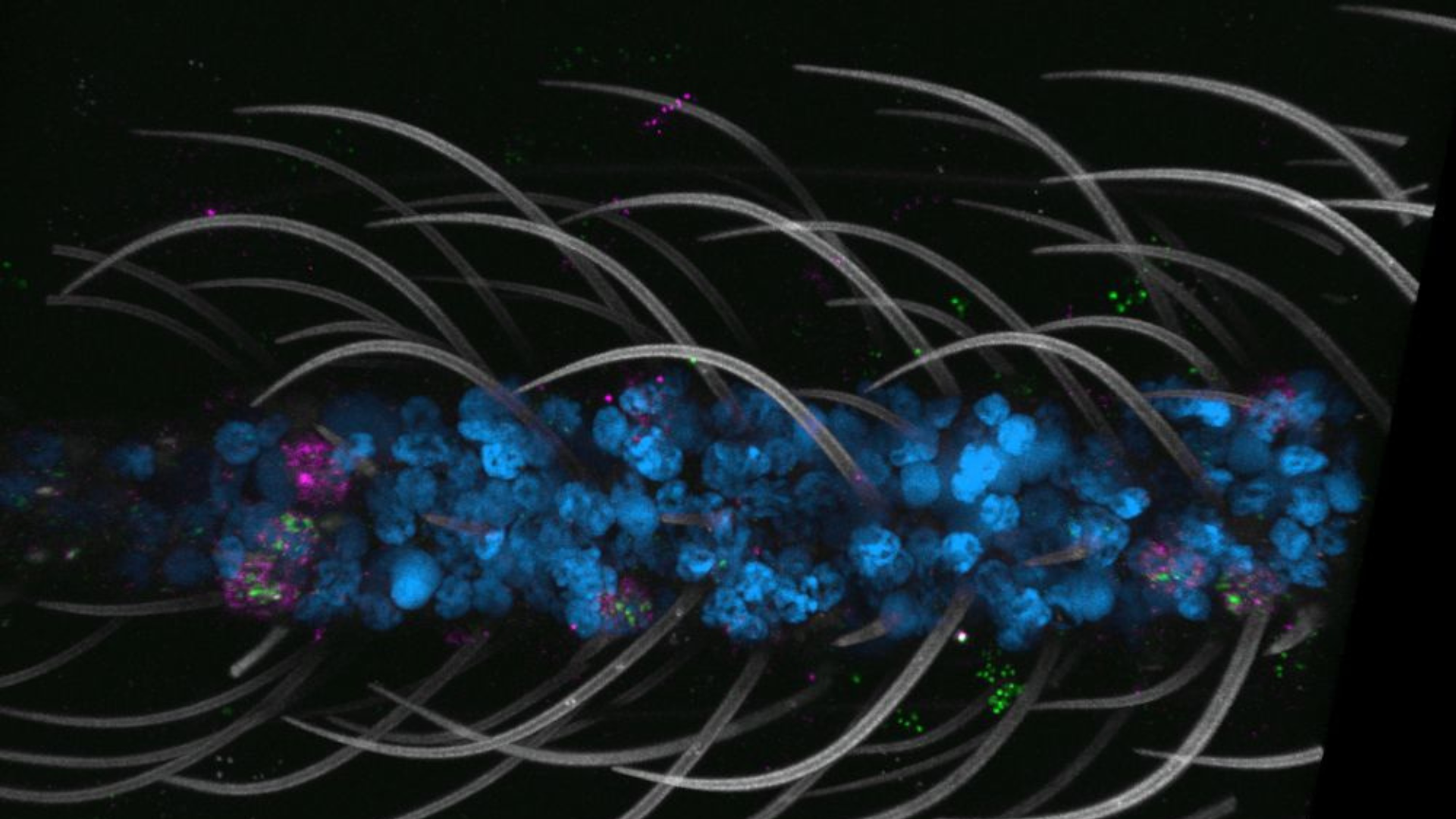
Researchers from Rockefeller University and an international team of experts have unveiled the first-ever cellular atlas of the Aedes aegypti mosquito, a species recognized as one of the most significant global health threats. Announced on October 30, 2023, the Mosquito Cell Atlas provides a detailed view of gene expression across 19 different tissues, revealing critical insights into this mosquito’s biology.
This groundbreaking atlas highlights that no other mosquito species transmits as many diseases. For decades, scientists have focused on the female Aedes aegypti due to its role as a vector for numerous pathogens, including those causing dengue fever and Zika virus. As a result, previous research often overlooked the male mosquito, leading to a significant knowledge gap.
Leslie Vosshall, a prominent researcher in the field, noted, “This is a comprehensive snapshot of what every cell in the mosquito is doing as far as expressing genes. It’s a real achievement because we profiled so many different types of tissues in both males and females.” The dataset, which includes profiles of over 367,000 cell nuclei, is freely accessible to both the public and scientific community, fostering further research and discovery.
Addressing Research Gaps
Prior to the creation of this atlas, research on Aedes aegypti was often disjointed, focusing on individual organs or tissues. This fragmented approach contributed to an incomplete understanding of the mosquito’s cellular biology. The researchers employed a technique known as single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) to compile their findings, examining tissues related to vital biological functions such as sensation, viral infection, reproduction, and the central nervous system.
The atlas successfully identified 69 distinct cell types, organized into 14 major categories. Many of these cell types had not been previously observed. Notably, the research revealed that polymodal sensory neurons—cells that detect environmental cues like temperature and taste—are more widespread than previously understood. Initially identified in the antennae, these chemoreceptors were found throughout the mosquito’s body, enhancing its ability to seek hosts and reproduce.
Nadav Shai, a senior author of the study, explained, “Together they enable mosquitoes to be really good at what they do—seek hosts, feed on them, and reproduce.” This enhanced sensory perception is vital for the mosquito’s survival, allowing it to identify sweetness and fresh water sources.
New Insights into Mosquito Behavior
The atlas also provided unexpected insights into the physiological changes that occur in female mosquitoes after they consume a blood meal. Following this meal, a female mosquito’s interest in seeking out hosts diminishes as her focus shifts to developing eggs. The research demonstrated significant alterations in gene expression within the brain during this period, revealing that glial cells—support cells that constitute less than 10% of the brain’s cellular makeup—undergo substantial rewiring.
Interestingly, the atlas indicated limited sexual dimorphism at the cellular level, despite the many recognized differences in morphology and behavior between male and female mosquitoes. The researchers found that the cellular composition of male and female mosquitoes is largely identical, with notable exceptions being the reproductive organs and a few clusters of sex-specific cells.
The Mosquito Cell Atlas is set to serve as a vital global resource, paving the way for future research that could lead to breakthroughs in controlling mosquito-borne diseases. The comprehensive study was published in the journal Cell on the same day as its announcement, marking a significant milestone in entomological research.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods