Science
Scientists Discover New Ice Form, Ice XXI, at Room Temperature
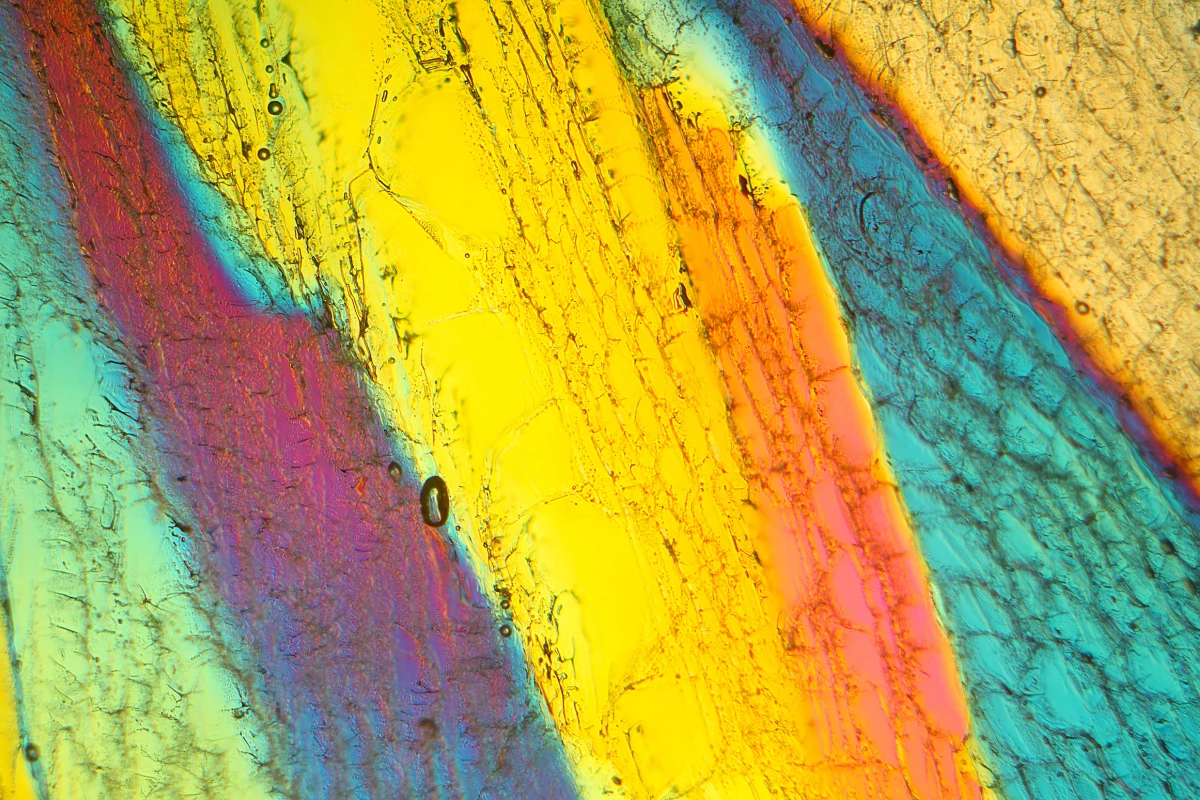
Researchers at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) have unveiled a groundbreaking new form of ice, officially named ice XXI, which can form at ambient temperatures. This discovery adds to the existing array of over 20 known types of ice, each characterized by unique internal structures. The findings have significant implications for our understanding of water’s behavior in extreme environments, which could extend to icy moons and other celestial bodies.
Ice is not simply frozen water; it can take on multiple forms depending on temperature and pressure conditions. While many ice types require extreme conditions to form, ice XXI emerges under relatively moderate pressures of around 1.6 gigapascals. The research team observed that water does not freeze in a straightforward manner but instead undergoes multiple cycles of freezing and melting before settling into a known phase, such as ice VI.
Unique Experimental Techniques Reveal New Insights
The breakthrough came through sophisticated experimental methods that combined diamond anvils with high-powered X-ray lasers. The researchers monitored how super-compressed water behaved at room temperature, capturing the phase transitions with remarkable precision. By adjusting pressure rapidly, they were able to track the transformation of water into ice XXI, revealing that this new type of ice has a distinct body-centered tetragonal crystal structure.
According to Geun Woo Lee, a scientist at KRISS, the rapid compression of water allows it to remain in liquid form at pressures where it would typically crystallize into ice VI. This unique behavior highlights the complexities of ice formation and the conditions under which ice XXI can exist.
The experiments utilized real-time monitoring tools, including high-speed cameras and laser sensors, to observe changes in structure, pressure, and volume. The X-ray beams employed at European XFEL provided the necessary detail to identify the exact moment water transformed into ice XXI. This innovative approach also revealed that there are at least five distinct pathways for water to crystallize, even at room temperature.
Implications for Understanding Ice and Planetary Science
The discovery of ice XXI may offer valuable insights into the conditions on icy moons and other potentially habitable environments beyond Earth. As Rachel Husband, another researcher involved in the study, noted, the findings suggest that a greater number of high-temperature metastable ice phases may exist. This could significantly enhance our understanding of the composition of celestial bodies that harbor water in some form.
The study, published in Nature Materials, demonstrates the ongoing quest to unravel the complexities of water and ice. The implications of this research extend beyond academic curiosity; they may provide critical information for planetary science and the search for extraterrestrial life. The ability to comprehend how water behaves under various pressures and temperatures could ultimately shape our understanding of other worlds.
As scientists continue to explore the intricate behavior of water and its various forms, the discovery of ice XXI stands out as a pivotal milestone in the field. This research not only enriches our scientific knowledge but also opens new avenues for future exploration and inquiry into the mysteries of ice and its role in the universe.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide