Science
Researchers Identify Early Parkinson’s Disease Biomarkers in Blood

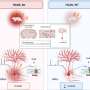
A team of researchers from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden has made significant strides in the early detection of Parkinson’s disease. They successfully identified specific biomarkers in the blood that indicate the disease’s onset, even before considerable brain damage occurs. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way Parkinson’s is diagnosed and monitored.
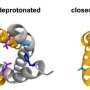
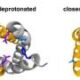
The research indicates that biological processes linked to Parkinson’s leave identifiable traces in the blood. However, these biomarkers are detectable only for a limited time, making timely testing crucial. Early diagnosis can lead to better management of the disease, potentially improving the quality of life for patients.
Breakthrough in Early Detection
Parkinson’s disease affects millions worldwide, causing progressive neurological decline. Traditionally, diagnosing the disease has relied heavily on observable symptoms, which often appear only after significant neurological impairment has taken place. The ability to identify biomarkers in the blood shifts this paradigm, allowing for earlier and more effective intervention strategies.
According to the research team, the biomarkers are linked to specific neurodegenerative processes. These markers can be detected in blood samples from individuals in the initial stages of the disease. This finding highlights the importance of developing screening tools that can be used in clinical settings to identify at-risk individuals.
Implications for Treatment and Management
The implications of this research extend beyond mere diagnosis. By identifying Parkinson’s in its earliest stages, healthcare providers can implement treatment plans sooner, potentially slowing disease progression and enhancing patient outcomes. Early intervention strategies could include lifestyle changes, medication, and targeted therapies that might mitigate symptoms before they escalate.
This advancement in biomarker research could also pave the way for future studies aimed at understanding the underlying mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease. As scientists continue to explore these biological markers, there is hope for developing more effective therapies, ultimately transforming how the disease is managed.
The findings from Chalmers University represent a significant milestone in the quest to combat Parkinson’s disease. Continued research will be essential to validate these biomarkers and integrate them into standard clinical practice, ensuring that patients receive timely and effective care.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2