Science
Research Reveals Vulnerability of Shield Tunnels to Surcharge Loading
Recent research has identified significant vulnerabilities in shield tunnels used in urban metro systems, particularly under conditions of accidental surcharge loading. Conducted by a team from Tongji University, the study highlights the potential risks posed by this man-made hazard, which can lead to structural issues such as horizontal convergence, joint dislocations, and leakage.
Traditionally, studies on tunnel vulnerability have focused primarily on seismic hazards, often neglecting the impact of extreme surcharge loading. This oversight can result in inaccurate evaluations of tunnel safety. Moreover, many existing studies rely on single damage indicators and fail to take into account the uncertainties associated with soil parameters and tunnel burial depths, which diminishes their relevance in practical applications.
Developing a Comprehensive Assessment Framework
The research, titled “Vulnerability Analysis of Shield Tunnels Under Surcharge Loading,” proposes a novel framework for assessing the damage state of shield tunnels when subjected to sudden and extreme surcharge conditions. The team, comprising Zhongkai Huang, Hongwei Huang, Nianchen Zeng, and Xianda Shen, developed a two-dimensional numerical model using ABAQUS to simulate shield tunnels in soft soil. This model was validated with data collected from field monitoring.
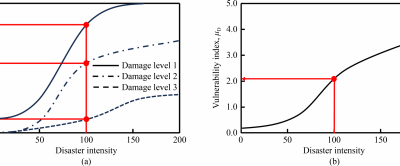
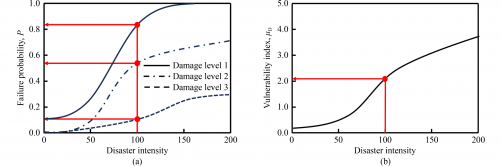
In their analysis, the researchers selected joint opening—categorized by locations at the tunnel crown, springline, and invert—as well as horizontal convergence as key damage indices. They established clear classifications of damage states including none, minor, moderate, extensive damage, and collapse. To quantify the risk of damage, they employed Monte Carlo simulations to generate fragility curves, which describe the probability of exceeding certain damage states, and vulnerability curves, which illustrate expected levels of damage.
Key Findings and Real-World Application
The research revealed critical insights into the vulnerabilities of tunnels at varying depths: shallow tunnels (8 m), moderately deep tunnels (16 m), and deep tunnels (30 m). Notably, Joint 2, located at the springline, exhibited the highest probability of failure under the same surcharge conditions. Furthermore, moderately deep tunnels demonstrated increased vulnerability when surcharge levels exceeded 50 kPa. Deep tunnels, while initially more vulnerable due to heightened soil and water pressures, were found to be less responsive to increases in surcharge.
The practical implications of this research were evident in its application to a real case involving the Shanghai Metro Line 2. The framework successfully identified high-risk sections, specifically ring numbers 350–390 and 550–590, allowing for targeted mitigation measures such as grouting and the installation of bonded AFRP or steel plates.
This study marks a significant advancement in understanding the structural integrity of shield tunnels under surcharge loading. The complete findings are documented in the paper “Vulnerability Analysis of Shield Tunnels Under Surcharge Loading,” available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-025-1193-4.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoHarmonic Launches AI Chatbot App to Transform Mathematical Reasoning