Science
Fruit Fly Embryos Reveal DNA Reorganization Triggered by Crowding
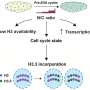
Research from the University of California, San Francisco has uncovered significant insights into how cellular crowding in fruit fly embryos leads to a crucial reorganization of DNA. This finding sheds light on the transition from rapid cell division to the formation of specialized cells, which are vital for the developing organism’s functions.
Understanding the mechanisms that govern embryonic development has long been a challenge for biologists. Following fertilization, embryos undergo rapid cell divisions, a process essential for early development. However, as these embryos transition to creating distinct cell types, the signals responsible for this shift remained largely unknown until now.
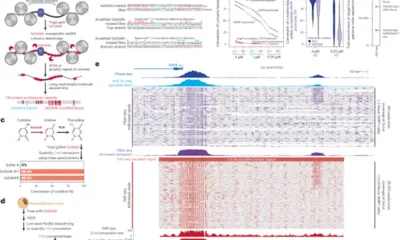
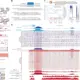
The researchers focused on the fruit fly, or Drosophila melanogaster, a model organism widely used in genetic studies. This study, published in March 2024, highlights how the physical environment within the embryo influences genetic organization. As cells become more crowded during early development, they trigger a series of changes in the DNA structure that are critical for specialization.
The study identified that the congestion of cells activates specific pathways that reorganize the DNA. This alteration plays a key role in determining which genes are expressed and when during the developmental process. Such insights could have far-reaching implications for our understanding of not only fruit fly development but also broader biological processes in other organisms.
David Schneider, a professor of biology at the University of California, San Francisco, emphasized the significance of these findings. “Understanding how cellular crowding influences DNA organization can help us comprehend the fundamental principles of development,” he stated. This research underscores the intricate relationship between physical conditions within cells and genetic regulation.
The implications of these findings extend beyond fruit flies. Understanding DNA organization in crowded cellular environments may provide insights into similar processes in human development and diseases. Researchers believe that unraveling these mechanisms could pave the way for better understanding genetic disorders and developmental anomalies.
As scientists continue to explore the complexities of embryonic development, this study represents a crucial step towards deciphering the signals that govern cellular specialization. The ongoing research could lead to innovative approaches in developmental biology and genetics, with potential applications in medicine and biotechnology.
In conclusion, the discovery of how cellular crowding impacts DNA reorganization in fruit fly embryos opens new avenues for research. This critical knowledge enhances our understanding of developmental biology and may ultimately contribute to advancements in health sciences. The study not only highlights the importance of model organisms in scientific research but also the intricate dynamics that govern life at the cellular level.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods