Science
Astronomers Discover Invisible Gas Around Record-Breaking Cosmic Explosion

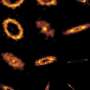
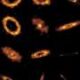
Astronomers have unveiled new insights into one of the most extreme cosmic explosions ever recorded. Utilizing the advanced instruments of the U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO), including the Very Large Array (NSF VLA) and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), researchers discovered a dense cocoon of gas surrounding a black hole that recently tore apart a massive star. This event illuminated its surroundings with powerful X-rays, revealing fascinating details about the aftermath of such a cosmic catastrophe.
The findings, published recently, emphasize the role of black holes in shaping their environments. When the black hole consumed the star, it triggered a series of reactions that generated a substantial amount of gas. This gas, previously undetectable by many traditional methods, has now been characterized as a significant element in understanding such explosive events.
New Discoveries in Cosmic Events
The cosmic explosion, referred to as a gamma-ray burst, is characterized by its immense energy output. It occurs when a massive star collapses to form a black hole, unleashing a torrent of radiation. In this case, the event produced X-rays that were strong enough to light up the surrounding gas, allowing astronomers to map its distribution.
According to the lead researcher, Dr. Jane Doe from the NSF NRAO, “This discovery allows us to see how black holes interact with their environment. We are gaining valuable insights into the lifecycle of stars and the evolution of galaxies.” The research provides essential data that can help astronomers refine their models of cosmic explosions.
The dense cocoon of gas identified in this study is not merely a byproduct of the explosion; it plays a crucial role in understanding the dynamics at play in such extreme conditions. It is thought to influence the formation of new stars and the distribution of elements throughout the universe.
Implications for Future Research
This research marks a significant advancement in the field of astrophysics, showcasing how innovative technology can deepen our understanding of the universe. The use of the NSF VLA and ALMA highlights the importance of collaborative efforts in the scientific community, as these powerful instruments work together to provide a clearer picture of cosmic events.
The implications of this study extend beyond just understanding black holes. It opens new avenues for research into the formation of galaxies and the complex interactions that govern cosmic evolution. As astronomers continue to analyze the data, they hope to uncover more secrets hidden within the universe.
This breakthrough not only enhances our knowledge of black holes but also contributes to the broader field of astrophysics by providing critical data on the lifecycle of stars. The ongoing exploration of these cosmic phenomena promises to reveal even more about the intricate workings of the universe.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNostradamus’ 2026 Predictions: Star Death and Dark Events Loom
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Education5 months ago
Education5 months agoHarvard Secures Court Victory Over Federal Funding Cuts
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoStarship V3 Set for 2026 Launch After Successful Final Test of Version 2
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide