Education
University Engineers Uncover Flaw in Rover Testing Methodology
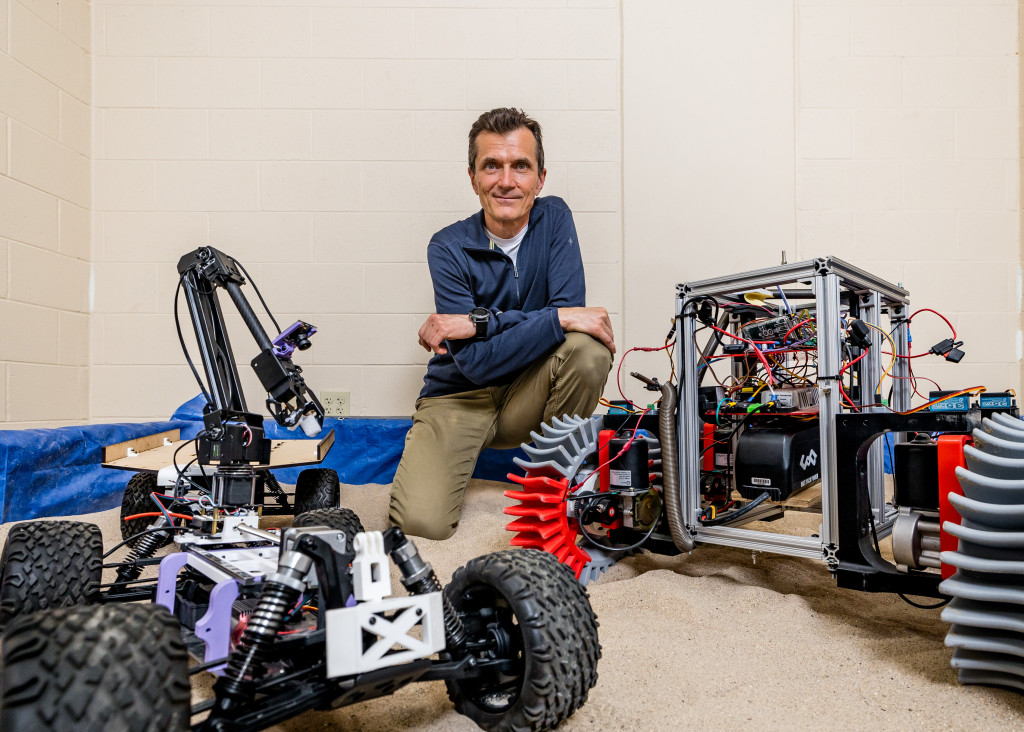
Engineers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have identified a critical flaw in the testing methodology used for robotic space rovers. This discovery stems from their work on the VIPER rover, a lunar mission prototype. The findings could significantly enhance future missions by improving the understanding of how rovers navigate extraterrestrial terrains.
When rovers, such as the Mars rover Spirit, become immobilized in soft terrain, engineers on Earth must intervene remotely. This labor-intensive process can delay exploratory missions. In 2009, Spirit became permanently stuck in Martian sand, highlighting the need for better terrain testing before deployment.
New Insights from Computer Simulations
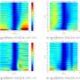
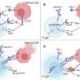
The research team, led by mechanical engineering professor Dan Negrut, employed advanced computer simulations to address the issue. Their approach utilized Project Chrono, an open-source physics simulation engine developed at the university. The team discovered that traditional testing methods, which simulate rovers at a fraction of their actual mass, do not adequately account for the different gravitational forces affecting both the rover and the surface it traverses.
Researchers have long derived insights by testing lightweight prototypes in desert environments. These tests aimed to mimic lunar conditions, where the gravitational pull is six times weaker than that on Earth. However, the team realized that they had overlooked a key factor: the effect of Earth’s gravity on sand. On our planet, gravity compresses sand, making it more stable and less likely to shift under a rover. In contrast, lunar sand is “fluffier,” presenting unique challenges for mobility.
“Considering both the rover’s weight and the sand’s response to gravity gives us a clearer picture of its performance on the moon,” Negrut explained. “Our findings underscore the importance of physics-based simulations for understanding rover mobility on granular surfaces.”
Implications for Future Missions and Engineering
The research has been published in the Journal of Field Robotics, emphasizing its significance for both space exploration and terrestrial applications. It was part of a NASA-funded initiative to simulate the VIPER rover and its potential performance on the moon.
The implications extend beyond space missions. The Chrono simulation engine has been utilized by numerous organizations, including the U.S. Army, to analyze complex mechanical systems, from military vehicles to precision instruments.
Negrut expressed pride in the impact of their research. “It’s rewarding that our findings can help solve various real-world engineering challenges,” he stated. “Producing industrial-strength software used by NASA is a significant achievement for a university lab.”
The Chrono engine remains free and publicly available, allowing for widespread use and continuous improvement. Negrut noted that open-source development drives innovation, as ideas can be quickly adopted by others in the field. Ongoing support from the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Army Research Office has been instrumental in sustaining their work.
As the team continues to enhance their simulation software, the future of robotic exploration looks promising. By refining testing methodologies, they aim to prevent rovers from becoming stuck on distant celestial bodies, ensuring successful missions that expand our understanding of the universe.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods