Science
Two Newly Discovered Comets to Illuminate Night Skies This Month
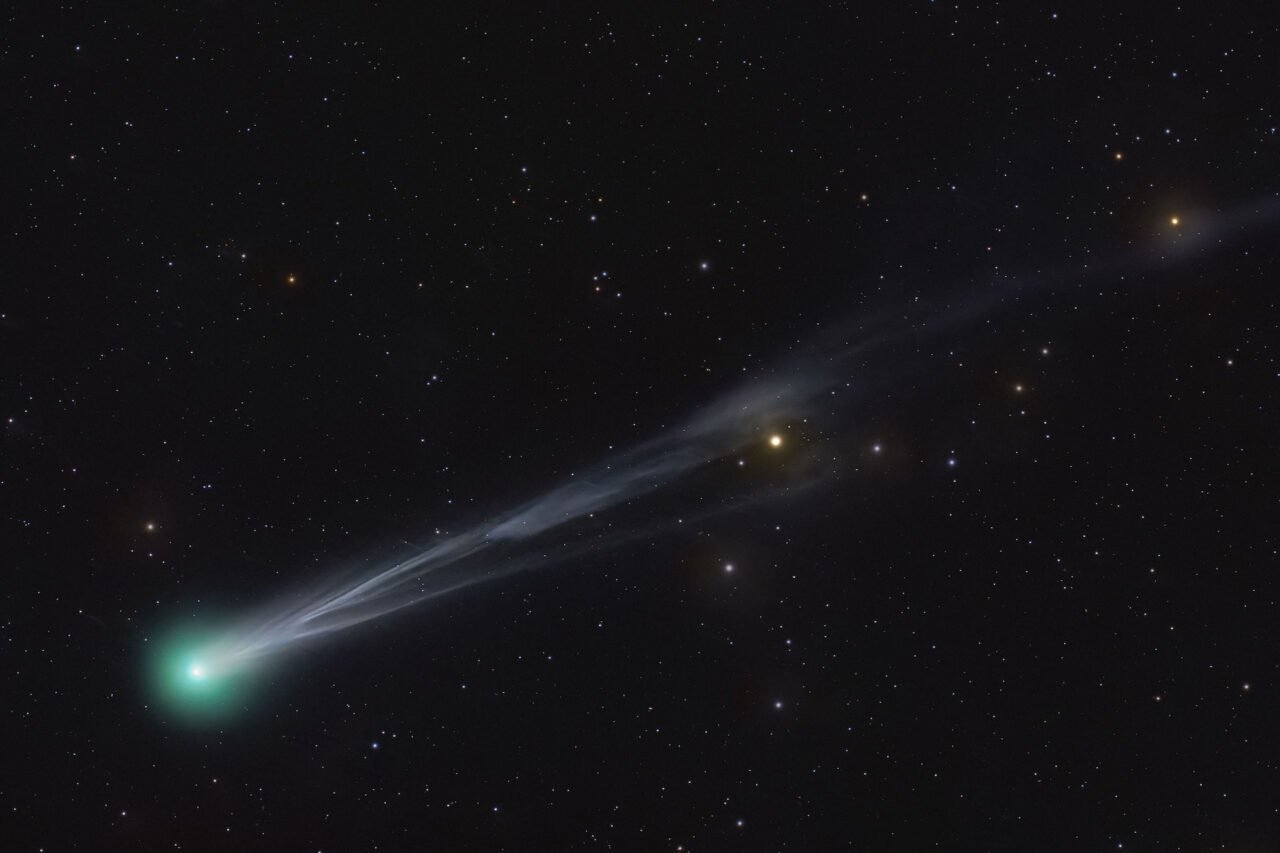

Skywatchers around the world have a rare opportunity this month as two newly discovered comets, C/2025 R2 (SWAN) and C/2025 A6 (Lemmon), are set to traverse the night skies. Both comets, which were identified in 2025, will make close approaches to Earth this month, enhancing their visibility. SWAN will reach its nearest point to Earth on October 19, 2025, while Lemmon will follow closely behind, approaching our planet on October 21, 2025. There is potential for both comets to be seen with the naked eye during this period.
Discovery and Characteristics
The comet Lemmon was first spotted in January 2025 at the Mt. Lemmon SkyCenter in Arizona’s Santa Catalina Mountains. It was observed traveling towards the inner solar system at remarkable speeds, reaching up to 209,000 kilometers per hour (approximately 130,000 miles per hour). In September, amateur astronomer Vladimir Bezugly discovered comet SWAN through images captured by the SWAN instrument on NASA’s SOHO satellite. As SWAN moved away from the Sun, it became significantly brighter, currently exhibiting a brightness magnitude of around 5.9, as reported by EarthSky.
At its closest approach, SWAN will be located approximately 24 million miles (or 39 million kilometers) from Earth, which is about a quarter of the distance between Earth and the Sun. The comet is currently visible in the southern skies but is gradually shifting northward, according to NASA.
Following its close approach, comet Lemmon will be positioned roughly half the distance between the Sun and Earth before rounding the Sun on November 8, 2025. As it continues to approach the Sun, Lemmon is expected to brighten further, with optimal visibility likely occurring around October 31 to November 1, according to EarthSky.
Viewing Opportunities
For those hoping to catch a glimpse of comet SWAN, the best viewing conditions are in the Southern Hemisphere. SWAN transitioned into the Libra constellation on September 28 and will move through Scorpius by October 10. Observers should look for SWAN near Beta Librae, the brightest star in Libra, around October 9 to 10. However, spotting this comet may be challenging due to its proximity to the setting Sun. Skywatchers should direct their gaze westward just after sunset for the best chance of viewing.
Conversely, comet Lemmon offers better visibility in the Northern Hemisphere. Throughout October, it will be situated near the Big Dipper, making it easier to observe. Early risers should look towards the eastern skies just before sunrise to catch a glimpse of Lemmon. By mid-October, the comet’s visibility is expected to improve, particularly on October 16, when it will pass near Cor Caroli, a binary star system in the northern constellation of Canes Venatici. During this period, Lemmon may also become visible to the naked eye, enhancing the excitement for skywatchers.
As both comets arrive, the celestial events present a unique opportunity for stargazers and astronomy enthusiasts to witness these remarkable visitors from the depths of space.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods