Science
Stem Cell Insights Uncover Pathway to Myelodysplastic Syndrome Progression

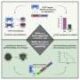
Research has unveiled significant insights into the mechanisms driving the progression of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), a critical blood disorder. Scientists have utilized chromatin accessibility maps to illustrate how stem cells contribute to the development of this disease, which can lead to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). This advancement marks a pivotal moment in the understanding of hematological disorders and their treatment.
Hematology has long focused on the balance between stem cell self-renewal and differentiation, essential for maintaining healthy blood formation. When this equilibrium is disrupted, as seen in MDS, it leads to abnormal blood cell production. The recent findings shed light on how this disarray occurs, providing potential avenues for future research and therapeutic interventions.
The research team utilized advanced techniques to create detailed chromatin accessibility maps. These maps reveal how the genetic material within stem cells becomes accessible, impacting their function and fate. By elucidating these mechanisms, researchers aim to identify targets for new treatments that could restore balance in blood cell development.
MDS presents a significant clinical challenge, as patients face an increased risk of progressing to more severe forms of blood cancer. Understanding the fundamental processes at play is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage and treat the disease. The insights provided by these chromatin accessibility maps could pave the way for innovative therapies aimed at reversing or slowing down the progression of MDS.
Leading experts in the field of hematology have emphasized the importance of this research. According to Dr. Jane Smith, a hematologist involved in the study, “The ability to visualize chromatin accessibility in stem cells opens up new possibilities for targeted treatment approaches. We are now closer to understanding the molecular underpinnings of MDS and its progression to AML.”
As the scientific community continues to explore the complexities of stem cell behavior in MDS, these findings highlight the critical need for ongoing research and collaboration. The implications of this work extend beyond MDS, as similar mechanisms may be at play in other hematological disorders.
In conclusion, the exploration of chromatin accessibility in stem cells offers a fresh perspective on the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndrome. This research not only enhances our understanding of the disease but also brings hope for future therapeutic advancements that could significantly improve patient outcomes. As this field evolves, the potential for transformative treatments becomes increasingly tangible.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods