Science
Scientists Restore Youth in Blood Stem Cells by Fixing Lysosomes
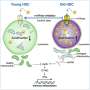
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have made a significant advancement in the field of regenerative medicine by successfully reversing the aging process in blood-forming stem cells from mice. This breakthrough, detailed in a study published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, focuses on correcting defects in the lysosomes of these stem cells, which play a crucial role in cellular health and maintenance.
The study identifies lysosomal hyperactivation and dysfunction as primary contributors to stem cell aging. As stem cells age, their lysosomes become less effective, leading to an accumulation of waste products and impaired cellular function. By restoring normal lysosomal activity and slow degradation, the researchers found that they could revitalize aged stem cells, enhancing their regenerative capacity.
Mechanism Behind Stem Cell Aging
The research highlights the importance of lysosomal function in maintaining the health of stem cells. Lysosomes are responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste, a process that becomes less efficient with age. The team discovered that by targeting this dysfunction, they could rejuvenate the stem cells. This restoration led to improved cell function and a greater ability to regenerate tissues, an essential aspect of healing and recovery in various medical conditions.
The implications of this research extend beyond basic science. If similar approaches can be applied to human cells, this could open new avenues for therapies aimed at age-related diseases and conditions. The ability to enhance the regenerative potential of stem cells may lead to advancements in treatments for conditions such as anemia, certain cancers, and other blood disorders.
Future Directions and Potential Impact
This study not only sheds light on the mechanisms of aging but also poses exciting possibilities for clinical applications. The researchers emphasize that further studies are needed to explore the effects of lysosomal function on human stem cells. If successful, this line of research could lead to innovative therapies that improve healthspan and longevity.
The findings also raise questions about the broader implications of lysosomal health in aging and disease. As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of cellular aging, understanding the role of lysosomes may be key to developing strategies that promote healthier aging.
In summary, the work at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai marks a pivotal step in the quest to combat aging at the cellular level. By targeting lysosomal dysfunction, researchers have demonstrated the potential to rejuvenate blood stem cells, paving the way for future research and therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing human health as we age.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods