Science
Revolutionary Solid-State Solar Cells Emerge from Quiet Experiment
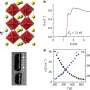
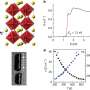
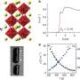
The development of the first solid-state solar cell based on a perovskite semiconductor has the potential to significantly alter the landscape of solar power. This groundbreaking innovation originated from a studied experiment at Northwestern University, where researchers aimed to harness the unique properties of perovskite materials for improved energy conversion efficiency.
The journey began in 2012 when a research team led by Dr. Mercouri G. Kanatzidis focused on exploring the capabilities of perovskite semiconductors. Their findings have since laid the groundwork for advances in solar technology, as perovskite solar cells have consistently achieved higher efficiency rates compared to traditional silicon-based cells.
Significance of Perovskite Solar Cells
Perovskite solar cells are celebrated for their remarkable efficiency and lower production costs. These cells can be manufactured using simpler processes than those required for silicon cells, making them an attractive option for widespread implementation. The unique crystalline structure of perovskite allows for an optimal light absorption capacity, enabling higher energy conversion rates.
Since their inception, perovskite solar cells have surpassed previous records, achieving efficiencies above 25%. This efficiency has made them one of the leading contenders in the race for sustainable energy solutions. Moreover, the materials involved are abundant and less toxic than traditional photovoltaic materials, further enhancing their appeal for future applications in clean energy.
The quiet experiment at Northwestern University serves as a testament to the power of innovative research. The team’s findings have not only advanced scientific understanding but also sparked interest from various sectors, including private companies and governmental organizations, eager to integrate this technology into real-world applications.
Future Implications for Clean Energy
As the world grapples with climate change and seeks sustainable energy solutions, the implications of perovskite solar cells are profound. Their ability to provide efficient energy conversion at a lower cost could facilitate the transition toward renewable energy sources globally. This shift is crucial as countries aim to reduce their carbon footprints and meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
The ongoing research and development in this field continue to show promise. Collaboration among universities, government bodies, and private enterprises is expected to accelerate the commercialization of perovskite solar technology. With the foundation laid by the team at Northwestern University, the potential for these solid-state solar cells to contribute to a cleaner energy future is substantial.
In summary, the emergence of solid-state solar cells based on perovskite semiconductors stems from a focused research initiative that has now set the stage for significant advancements in solar power technology. The future of clean energy may well be shaped by innovations born from this quiet but impactful experiment.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods