Science
New Technique Revolutionizes Understanding of Chromatin Structures

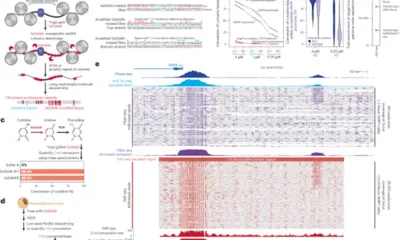
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking technique called Deaminase-Assisted single-molecule chromatin Fiber sequencing (DAF-seq), which offers unprecedented insights into how gene regulation occurs at the single-cell level in diploid organisms. This innovative method enables scientists to analyze the structures of chromatin fibers and the proteins bound to them, significantly enhancing our understanding of genetic heterogeneity.
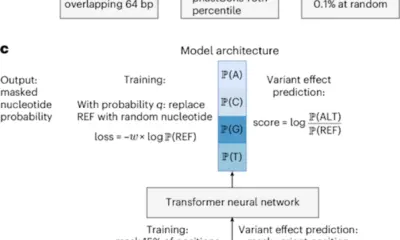
DAF-seq allows researchers to perform single-molecule footprinting at near-nucleotide resolution. This capability is vital for profiling chromatin states and the corresponding DNA sequences in individual cells. The technique illuminates the cooperative occupancy of proteins at regulatory elements and reveals the functional impacts of somatic variants and rare chromatin epialleles.
Seattle’s University of Washington is at the forefront of this research, with a team led by A.B. Stergachis. The new technique generates comprehensive maps of protein co-occupancy across 99% of each individual cell’s mappable genome. This level of detail uncovers extensive chromatin plasticity, demonstrating that chromatin activation can diverge by 61% between haplotypes within a single cell and by 63% between different cells.
The findings indicate that regulatory elements tend to be co-actuated along the same chromatin fiber in a manner that is dependent on distance, resembling the behavior of cohesin-mediated loops. The ability to characterize protein occupancy across entire chromosomes with such precision marks a significant advancement in genomics.
Research Funding and Collaborations
This project received support from various prestigious organizations, including the National Institutes of Health and the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative. The research team acknowledges the contributions of multiple collaborators, including the Northwest Genome Center for their assistance in sequencing, and the UW Mass Spectrometry Center for their support in mass spectrometry experiments.
The implications of this research are profound, potentially transforming the field of genetics. By providing a clearer understanding of how chromatin structures influence gene expression and regulation, DAF-seq paves the way for future studies on genetic disorders and therapeutic interventions.
In summary, DAF-seq represents a significant leap forward in genomic research, enabling scientists to dissect the complex interplay between DNA and proteins at a level of detail previously unattainable. As researchers continue to explore the intricacies of chromatin architecture, this method will undoubtedly play a crucial role in uncovering the fundamental mechanisms of gene regulation.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods