Science
Innovative Patch Pioneers Noninvasive Monitoring for Frog Conservation

Researchers from La Trobe University have developed a noninvasive method to monitor hormone levels in frogs, a significant advancement in efforts to conserve these vulnerable species. With global frog populations declining at a swift rate—41% of species are currently classified as threatened—this breakthrough addresses the urgent need for effective monitoring techniques in the face of challenges such as habitat loss, climate change, pollution, invasive species, and disease.
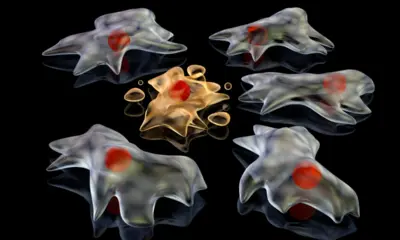
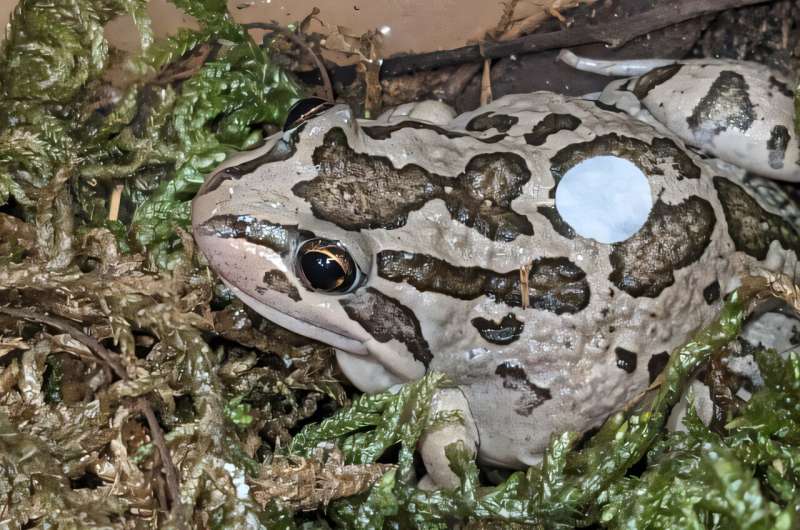
Traditionally, studying frog hormones has presented difficulties due to invasive methods like blood sampling, which can induce stress and negatively impact the animals. The innovative solution comes in the form of small patches that adhere to frog skin, collecting hormone-rich secretions without causing distress. This approach allows researchers to monitor the health and reproductive status of frogs more effectively.
Groundbreaking Research and Development
The research, carried out by the Wildlife Conservation and Reproductive Endocrinology Lab (WiCRE) at La Trobe University in collaboration with the University of Wollongong, showcases the potential of these dermal patches. The findings, published in Frontiers in Conservation Science, demonstrate that the patches can accurately measure hormone levels, providing vital insights into frog well-being without the need for invasive procedures.
Led by Dr. Alicia Dimovski and Dr. Kerry Fanson, the team optimized the patch method and confirmed its reliability through tests involving Blue Mountains tree frogs. Dr. Dimovski stated, “The study shows that dermal patches can effectively measure hormone levels in frogs with minimal disruption to the animal. This is a big step forward in helping us understand frog biology and improve conservation efforts.”
Frogs play a crucial role in ecosystems and are of significant cultural and intrinsic value. With many species threatened with extinction, there is an increasing demand for improved monitoring tools to assess their health. Dr. Dimovski expressed hope that this research would bolster conservation breeding programs and contribute to the long-term survival of these remarkable creatures.
Broader Implications for Amphibian Protection
The technique developed by the La Trobe team is not limited to a single frog species. It holds promise for application across various species, including the spotted marsh frog, enhancing the ability to monitor amphibian populations more broadly. This innovative advancement in conservation science could play a pivotal role in reversing the alarming trends affecting global frog populations.
As conservationists strive to combat the factors threatening amphibians, the introduction of noninvasive hormone monitoring represents a valuable tool in the ongoing effort to protect these essential organisms. The research underscores the importance of developing humane techniques that allow for effective monitoring without compromising the health or welfare of the animals involved.
For further details, the study titled “Validation of dermal patches as a non-invasive tool for monitoring amphibian steroid hormones” can be accessed in Frontiers in Conservation Science. The findings highlight a promising direction for future research and conservation strategies aimed at safeguarding frog populations worldwide.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoOpenAI to Implement Age Verification for ChatGPT by December 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAnalysts Project Stronger Growth for Apple’s iPhone 17 Lineup
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods