Science
Groundbreaking Biology Discoveries Transforming Research Landscape

Recent advancements in biological research have unveiled innovative breakthroughs that hold the potential to significantly impact human health and environmental conservation. These discoveries, spanning gene therapy to artificial intelligence, illustrate the dynamic nature of the scientific field.
Slowing the Progress of Huntington’s Disease
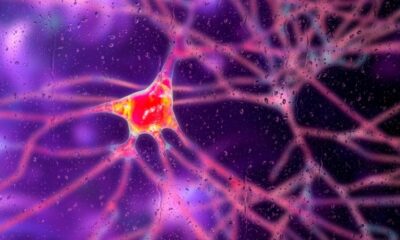
A significant stride has been made in treating Huntington’s disease, a hereditary neurodegenerative disorder known for its devastating effects on both mental and physical health. Researchers have developed a gene therapy, named AMT-130, which has shown the ability to slow disease progression by up to 75%. This novel therapy represents a breakthrough in a field where treatment options have been largely limited.
According to Scientific American, the treatment involves a surgical procedure lasting between eight to ten hours, during which a genetically modified virus is introduced into the brain. This virus functions like a microscopic delivery system, infusing a new DNA sequence into brain cells. Neurologist Victor Sung highlighted the importance of this development, stating, “We’ve had so many failures, and there’s been a lot of heartbreak over many years in this community. So to have something that at least really appears to be having [an] impact is really significant.” Currently, AMT-130 is undergoing clinical trials and is not yet available for widespread use.
Innovations in Understanding Cellular Mechanisms
In another significant advancement, researchers have introduced a method that enhances the understanding of cellular processes without invasive techniques. A study published in Nature Communications describes how scientists can use natural proteins as sensors to monitor their cellular environment. This approach allows for accurate observations of protein interactions and behaviors within cells.
According to Cornell University, the method employs flavoproteins, which possess magnetic properties detectable through electron spin resonance spectroscopy. This technique is particularly beneficial for studying biological mechanisms that may be linked to diseases such as cancer or infections. As Brian Crane, a professor in Cornell’s Department of Chemistry, explained, “One could conceivably track the assembly of a virus using this method to understand how and where its components are built within cells.”
Advancements in Reproductive Technology for Endangered Species
A pioneering achievement in reproductive science has emerged with the successful creation of the world’s first kangaroo embryo via in vitro fertilization (IVF). This development could play a crucial role in conserving endangered species in Australia. Researchers utilized a technique known as intracytoplasmic sperm injection, where a single sperm is directly injected into a mature egg.
While the eastern grey kangaroo is not currently endangered, the research aims to support the preservation of various marsupial species, including koalas and Tasmanian devils. Andres Gambini, the lead researcher, emphasized the urgency of this work, stating, “Our ultimate goal is to support the preservation of endangered marsupial species.” Australia has faced a concerning extinction rate, attributed to the unique endemic species that populate the continent.
Uncovering Ancient Microbial DNA
Researchers have also made remarkable discoveries in the field of ancient DNA, sequencing the genetic material of various mammoths as well as identifying microbial DNA associated with them. A study published in the journal Cell reveals insights into the lives of these creatures over a million years ago.
The team sequenced DNA from 440 mammoths, including previously unsequenced specimens, and identified 310 microbial groups that inhabited their tissues. While many of these microbes appeared after the mammoths’ extinction, six groups likely lived alongside them, influencing their digestion and immune responses. The potential applications of this methodology extend to other well-preserved remains, such as ancient horses and cave bears, according to Earth.com.
Virtual Laboratories Powered by AI
The integration of artificial intelligence into laboratory research represents another frontier in scientific exploration. A recent study published in Nature demonstrates how large language models (LLMs) can simulate the thought processes of leading scientists. This innovative approach could streamline research and hypothesis development.
Researchers trained AI models to emulate scientific reasoning, enabling them to devise new solutions and collaborate effectively. The virtual lab created by the researchers successfully proposed a novel vaccine basis for COVID-19, utilizing nanobodies in its design. James Zou, an associate professor of biomedical data science, remarked, “Good science happens when we have deep, interdisciplinary collaborations where people from different backgrounds work together.” This advancement could significantly enhance the pace of research and innovation in various fields.
The recent breakthroughs in biology not only highlight the advancing frontiers of scientific inquiry but also underscore the potential for transformative applications that could address pressing health and environmental challenges. As these discoveries continue to evolve, they reflect the relentless pursuit of knowledge and the hope for a better future.
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscover the Top 10 Calorie Counting Apps of 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoBella Hadid Shares Health Update After Treatment for Lyme Disease
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoErin Bates Shares Recovery Update Following Sepsis Complications
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDiscover How to Reverse Image Search Using ChatGPT Effortlessly
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscover 2025’s Top GPUs for Exceptional 4K Gaming Performance
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoElectric Moto Influencer Surronster Arrested in Tijuana
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoMeta Initiates $60B AI Data Center Expansion, Starting in Ohio
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoRecovering a Suspended TikTok Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoTested: Rab Firewall Mountain Jacket Survives Harsh Conditions
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoBelton Family Reunites After Daughter Survives Hill Country Floods
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoHarmonic Launches AI Chatbot App to Transform Mathematical Reasoning
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoUncovering the Top Five Most Challenging Motorcycles to Ride